Summary of Portuguese colonization of Angola (1575-1975)
Uncover the centuries-long story of Portuguese influence in Angola's history.
How Do You Learn Best?
Learn by Reading
Immerse yourself in the 10-minute visual lesson for a comprehensive understanding of the topic.
Learn by Reviewing
Jump directly to the key facts, timeline, and vocabulary lists to build a solid foundation of details.
Learn by Doing
Challenge yourself! Jump straight into the interactive games to learn by trial, error, and discovery.
Portuguese colonization of Angola in 10 Minutes

Introduction



Paulo Dias de Novais

Queen Nzinga

António de Oliveira Salazar

Agostinho Neto

Early Portuguese Exploration

Establishment of Portuguese Colonies

Expansion of Portuguese Rule

Colonial Administration and Economy

Resistance and Rebellion

Independence Movements

Angolan War of Independence

Transition to Independence

Post-Independence Challenges

Legacy of Portuguese Colonization
Lesson Details & Resources
In a Nutshell
- What: Portuguese colonization of Angola (1575-1975)
- When: 1575-1975
- Who: Portuguese colonizers, Angolan indigenous peoples
- Outcome: Long period of Portuguese control and exploitation, leading to Angolan independence in 1975
Famous Figures in the Portuguese colonization of Angola
-
Paulo Dias de Novais
Paulo Dias de Novais was a Portuguese explorer and colonial administrator who founded the city of Luanda in Angola.
-
Agostinho Neto
Agostinho Neto was a poet and politician who became the first President of Angola after its independence from Portugal in 1975.
-
António de Oliveira Salazar
António de Oliveira Salazar was the Prime Minister of Portugal during much of the colonial period in Angola, known for his authoritarian rule.
-
Jonas Savimbi
Jonas Savimbi was a leader of the National Union for the Total Independence of Angola (UNITA) during the Angolan Civil War, which followed independence.
-
Amália Rodrigues
Amália Rodrigues was a famous Portuguese fado singer who often performed in Angola during the colonial period.
Timeline of Portuguese colonization of Angola
Portuguese establish trading posts along the coast of Angola
Portuguese formally colonize Angola
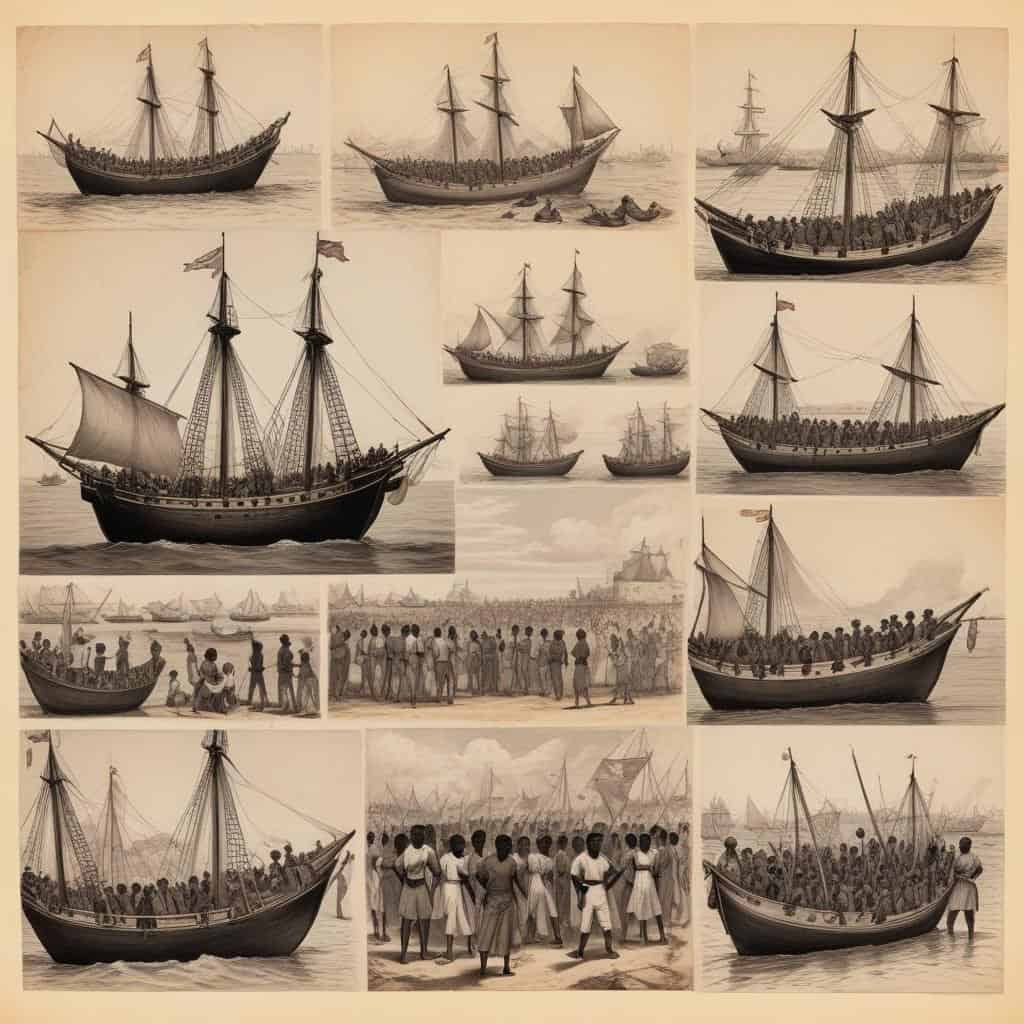
Angola becomes a major source of slaves for Portuguese colonies in the Americas
Portugal signs the Treaty of Vienna, recognizing Portuguese control over Angola
Angolan War of Independence begins
Angolan independence recognized by Portugal
Civil War breaks out in Angola between MPLA, UNITA, and FNLA
Cuban troops arrive in Angola to support MPLA
South African troops intervene in Angola on the side of UNITA
Portugal recognizes Angola's independence
Ceasefire agreements signed between MPLA, UNITA, and FNLA
Peace agreements signed in Angola
Angola becomes one of the fastest-growing economies in the world
Angola becomes a member of OPEC
Angola surpasses Nigeria as Africa's top oil producer
Angolan President José Eduardo dos Santos steps down after 38 years in power
Angola holds national elections
João Lourenço becomes President of Angola
Angola begins economic reforms to diversify its economy
Angola experiences economic challenges due to drop in oil prices
Vocabulary List
- Colonization
- Portuguese colonization of Angola began in 1575 and lasted until 1975.
- Exploitation
- The Portuguese exploited the resources of Angola, including minerals and labor.
- Slavery
- The Portuguese brought African slaves to Angola to work on plantations.
- Missionaries
- Portuguese missionaries played a role in spreading Christianity in Angola.
- Resistance
- Angolans resisted Portuguese colonization through armed uprisings and rebellions.
- Independence
- Angola gained independence from Portugal in 1975 after years of struggle.
- Civil war
- After independence, Angola was plagued by a civil war between different factions.
- Decolonization
- The decolonization of Angola marked the end of Portuguese rule in the country.
- Nationalism
- Angolan nationalism grew in response to Portuguese colonial rule.
- Post-colonial
- Angola faced challenges in the post-colonial period as it sought to rebuild and develop.
Key Facts
This is the information used in the fact matching game
- Angola was first colonized by the Portuguese in 1575.
- The Portuguese established Luanda as the capital of Angola in 1576.
- The Portuguese forcibly brought African slaves to Angola to work on plantations.
- Angola was a major source of slaves for the transatlantic slave trade.
- Portugal officially abolished slavery in Angola in 1836.
- Portugal declared Angola a colony in 1951.
- Portugal invested heavily in infrastructure in Angola, including railways and ports.
- Portugal imposed a system of forced labor on the Angolan population.
- Portugal fought a long and bloody war against Angolan independence movements in the 1960s and 1970s.
- Angola finally gained independence from Portugal in 1975.
- The Portuguese language remains widely spoken in Angola as a legacy of colonization.
- The Angolan Civil War, which lasted from 1975 to 2002, was a continuation of the struggle for independence.
- Portugal maintained close economic and political ties with Angola even after independence.
- The legacy of Portuguese colonization in Angola includes high levels of poverty and inequality.
- Portugal's withdrawal from Angola in 1975 led to a power vacuum and civil war.
- The MPLA (Popular Movement for the Liberation of Angola) emerged as the ruling party after independence.
- Portugal's colonial rule in Angola was marked by brutality and exploitation of the local population.
- Portugal's colonization of Angola had a lasting impact on the country's culture and politics.
- Portugal's rule in Angola was characterized by repression and resistance from the local population.
- The legacy of Portuguese colonization in Angola continues to shape the country's development and identity.
Analysis & Significance
Immediate Consequences
The Portuguese colonization of Angola in 1575 had immediate consequences on the local population, leading to the exploitation of resources and forced labor practices. The indigenous people faced violence, displacement, and loss of autonomy as the Portuguese established control over the region.
Long-Term Impact
The long-term impact of Portuguese colonization in Angola was profound, shaping the country’s history, culture, and economy for centuries to come. The legacy of colonization left a legacy of deep-rooted social inequalities, political instability, and economic dependency, which continue to impact Angola’s development and progress.
Cultural Significance Today
The cultural significance of Portuguese colonization in Angola is still felt today, influencing the country’s language, religion, and traditions. The legacy of colonization has also sparked debates about historical memory, national identity, and the need for reconciliation and healing in Angola’s post-colonial society.
Portuguese colonization of Angola Games
Take Your Learning Offline
Want a convenient, print-ready study guide for this lesson? Become a Memory Wizards Pro member to unlock the downloadable " Memory Scrolls" for this topic and our entire library!
- ✓ Complete Vocabulary Lists
- ✓ Key Facts & Timelines
- ✓ Beautifully Formatted for Print & Mobile




