Summary of Berlin Conference (1884-1885)
Uncover the secrets of the Berlin Conference and European colonialism.
How Do You Learn Best?
Learn by Reading
Immerse yourself in the 10-minute visual lesson for a comprehensive understanding of the topic.
Learn by Reviewing
Jump directly to the key facts, timeline, and vocabulary lists to build a solid foundation of details.
Learn by Doing
Challenge yourself! Jump straight into the interactive games to learn by trial, error, and discovery.
Berlin Conference in 10 Minutes

Introduction


King Leopold II of Belgium

Chancellor Otto von Bismarck

David Livingstone

Cecil Rhodes

Emperor Menelek II of Ethiopia

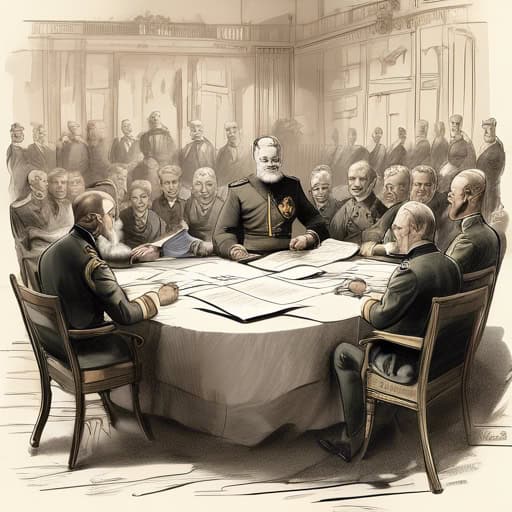
The Berlin Conference Begins

European Powers Divide Africa

The Scramble for Africa

Impact on African Peoples

Rise of European Empires

Resistance and Rebellion

Legacy of the Berlin Conference

Criticism of the Berlin Conference

Decolonization and Independence

Continued Impact on Africa

Lesson Details & Resources
In a Nutshell
- What: The division of Africa among European powers through diplomatic negotiations.
- When: 1884-1885
- Who: European colonial powers such as Britain, France, Germany, and Portugal.
- Outcome: Formalized the Scramble for Africa and laid down rules for the colonization of Africa.
Famous Figures in the Berlin Conference
-
Otto von Bismarck
Otto von Bismarck was the Chancellor of the German Empire and a key player in the Berlin Conference.
-
Leopold II of Belgium
Leopold II of Belgium was the king of Belgium and played a significant role in the colonization of Africa.
-
Cecil Rhodes
Cecil Rhodes was a British businessman and politician who had interests in southern Africa.
-
King Leopold II
King Leopold II of Belgium was heavily involved in the colonization of Africa, particularly in the Congo.
-
Jules Ferry
Jules Ferry was a French statesman who advocated for colonial expansion and was present at the Berlin Conference.
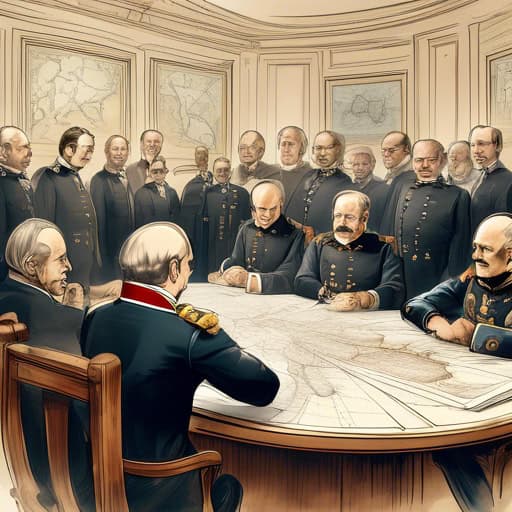
Timeline of Berlin Conference
European powers meet in Berlin to discuss the division of Africa
The conference officially begins with representatives from 14 countries present
The conference lasts for three months, ending on February 26, 1885
Agreements are made regarding the colonization and trade in Africa
The conference is chaired by German Chancellor Otto von Bismarck
The Scramble for Africa intensifies as a result of the conference
The conference results in the partitioning of Africa into colonies controlled by European powers
The conference establishes the principles of effective occupation and free trade in Africa
The conference leads to the colonization of almost the entire African continent by European powers
The conference is criticized for its lack of African representation and the arbitrary division of territories
The Berlin Act is signed, outlining the rules for European colonization in Africa
The conference marks the beginning of the New Imperialism era in Africa
The conference results in increased tensions and rivalries between European powers in Africa
The conference is seen as a key event in the history of colonialism and imperialism in Africa
The conference leads to the exploitation and oppression of African peoples by European colonizers
The legacy of the Berlin Conference continues to impact African countries and their development today
The conference sets the stage for future conflicts and struggles for independence in Africa
The Berlin Conference is considered a turning point in the history of Africa and its relationship with Europe
The conference highlights the power dynamics and inequalities between European and African nations
The conference results in the redrawing of borders and the displacement of indigenous peoples in Africa
Vocabulary List
- Scramble for Africa
- The Berlin Conference was a key event in the 'Scramble for Africa', where European powers divided up the continent for colonization.
- Colonialism
- The Berlin Conference formalized the process of colonialism in Africa by establishing rules for European powers to claim territories.
- Sphere of influence
- The Berlin Conference also allowed European powers to establish 'spheres of influence' in Africa, where they had exclusive economic and political control.
- Partition
- The Berlin Conference led to the partitioning of Africa into different territories controlled by European powers.
- Imperialism
- The Berlin Conference was driven by the imperialistic ambitions of European powers to expand their empires in Africa.
- Protectorate
- As a result of the Berlin Conference, some African territories became protectorates of European countries, where local rulers were allowed to remain in power but had to follow European policies.
- Nationalism
- The Berlin Conference sparked nationalist movements in Africa, as local populations resisted European colonization and sought independence.
- Berlin Act
- The Berlin Conference resulted in the signing of the Berlin Act, which established guidelines for European colonization in Africa and set the stage for further exploitation of African resources.
Key Facts
This is the information used in the fact matching game
- The Berlin Conference took place from November 15, 1884, to February 26, 1885.
- The conference was organized by German Chancellor Otto von Bismarck.
- The primary goal of the Berlin Conference was to regulate European colonization and trade in Africa.
- No African leaders were invited to the conference.
- The conference established the principle of effective occupation as a requirement for colonial claims in Africa.
- European powers agreed to respect each other's territorial claims in Africa and to work out any disputes peacefully.
- The Berlin Conference effectively divided Africa among European powers without considering the interests of African peoples.
- The conference led to the colonization and exploitation of Africa by European powers.
- The borders drawn at the Berlin Conference often ignored existing ethnic and cultural divisions in Africa.
- The conference set the stage for the Scramble for Africa, in which European powers rapidly expanded their colonial empires in Africa.
- The Berlin Conference contributed to the exploitation and oppression of African peoples by European colonial powers.
- The conference marked the beginning of formal European colonization in Africa.
- The Berlin Conference had long-lasting consequences for the political and social development of Africa.
- The conference resulted in the establishment of the Congo Free State, which was notoriously exploited by King Leopold II of Belgium.
- The Berlin Conference laid the groundwork for the colonization of Namibia by Germany.
- The conference led to the imposition of European languages, cultures, and institutions on African societies.
- Africans were not consulted or represented in the decisions made at the Berlin Conference.
- The Berlin Conference was a turning point in the history of Africa, marking the beginning of European colonial domination.
- The conference resulted in the partitioning of Africa into artificial territories controlled by European powers.
- The Berlin Conference reflected the imperial ambitions and rivalries of European powers in the late 19th century.
Analysis & Significance
Immediate Consequences
The Berlin Conference of 1884-1885 resulted in the partitioning of Africa among European powers, leading to increased colonization and exploitation of the continent. This event marked the formal beginning of the scramble for Africa, as European nations sought to carve out territories for themselves.
Long-Term Impact
The lasting impact of the Berlin Conference can be seen in the boundaries and divisions that were created in Africa, which continue to shape political and social dynamics on the continent. The conference also laid the groundwork for future conflicts and power struggles in Africa, contributing to the legacy of colonialism and its lasting effects.
Cultural Significance Today
The legacy of the Berlin Conference is still felt today in the form of ongoing debates about the impact of colonialism on Africa and the continuing struggles for independence and self-determination. It serves as a reminder of the lasting effects of European imperialism and the importance of understanding the historical context of global power dynamics.
Berlin Conference Games
Take Your Learning Offline
Want a convenient, print-ready study guide for this lesson? Become a Memory Wizards Pro member to unlock the downloadable " Memory Scrolls" for this topic and our entire library!
- ✓ Complete Vocabulary Lists
- ✓ Key Facts & Timelines
- ✓ Beautifully Formatted for Print & Mobile




