How Do You Learn Best?
Learn by Reading
Immerse yourself in the 10-minute visual lesson for a comprehensive understanding of the topic.
Learn by Reviewing
Jump directly to the key facts, timeline, and vocabulary lists to build a solid foundation of details.
Learn by Doing
Challenge yourself! Jump straight into the interactive games to learn by trial, error, and discovery.
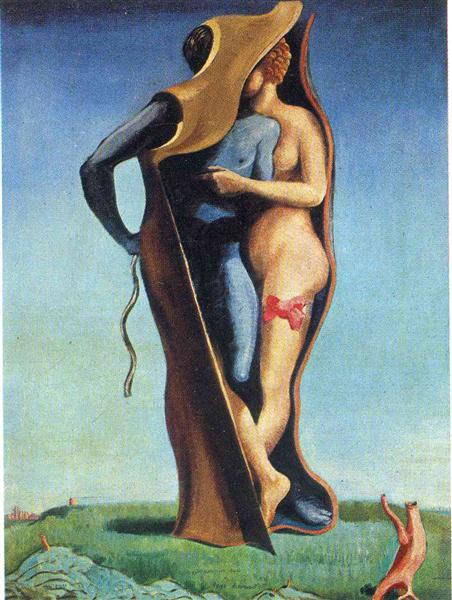
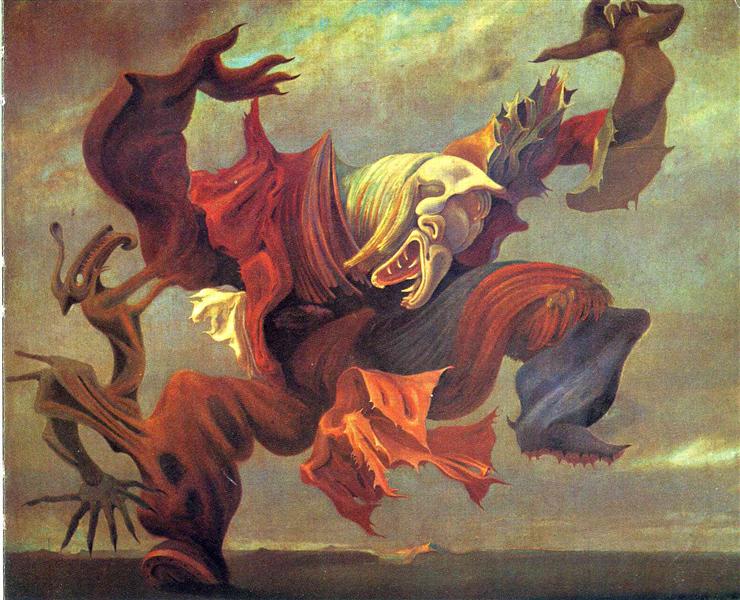
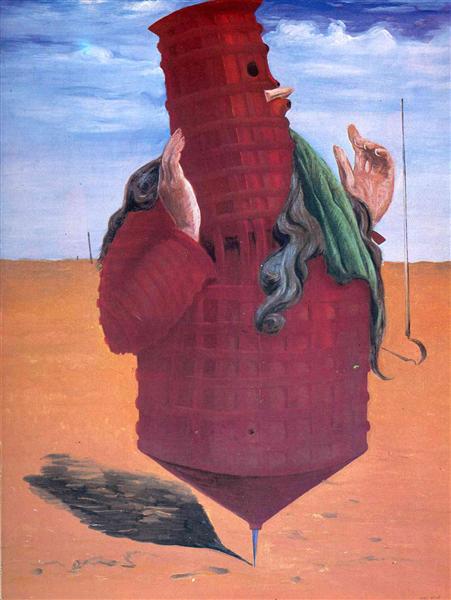
The Masterpiece: Ubu Imperator
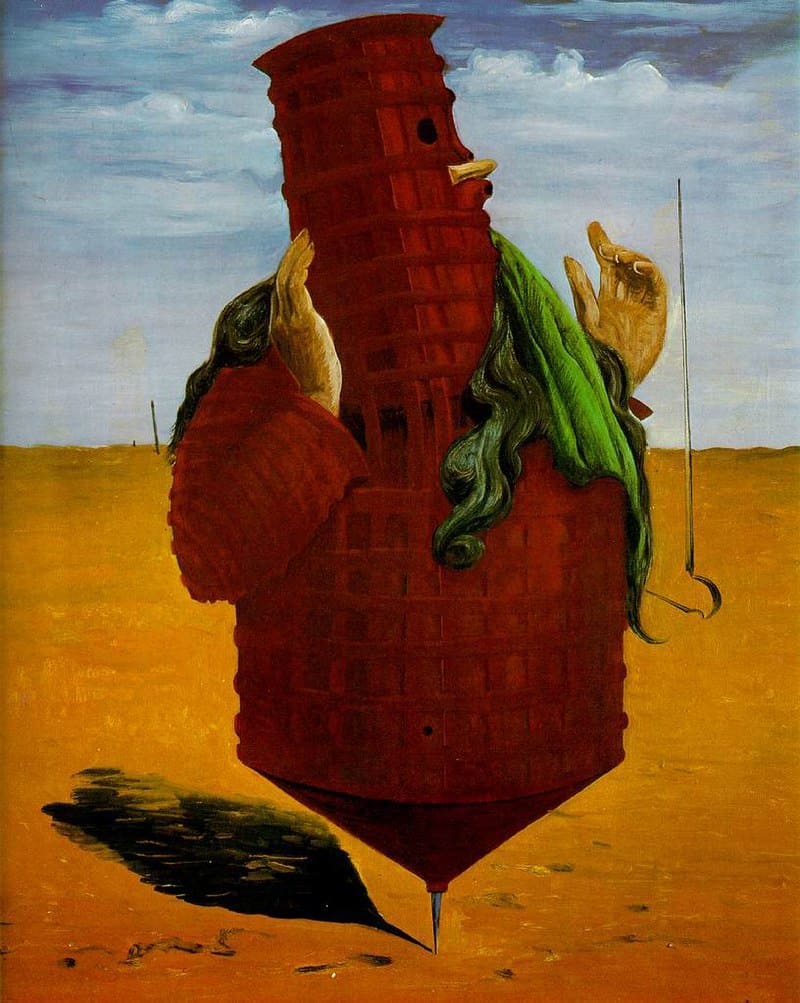

Deconstructing the Masterpiece
Monstrous Figure
The central red tower-like figure represents a grotesque symbol of authority, embodying the absurdity and instability of power.
Surreal Landscape
The dream-like setting enhances the otherworldly and fantastical nature of the artwork, adding to its surreal and mysterious quality.
Anthropomorphic Spinning Top
The anthropomorphic form of the spinning top figure blurs the line between human and object, creating a disorienting and unsettling effect.
Max Ernst: An Analysis in 10 Minutes

Introduction


The Birth of Surrealism

Exploring the Subconscious
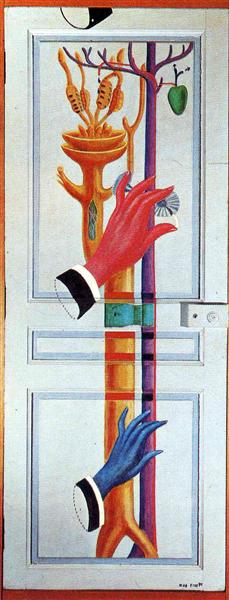
Inventing New Techniques

Creating Otherworldly Landscapes

Pushing the Boundaries of Art

Influencing Future Generations
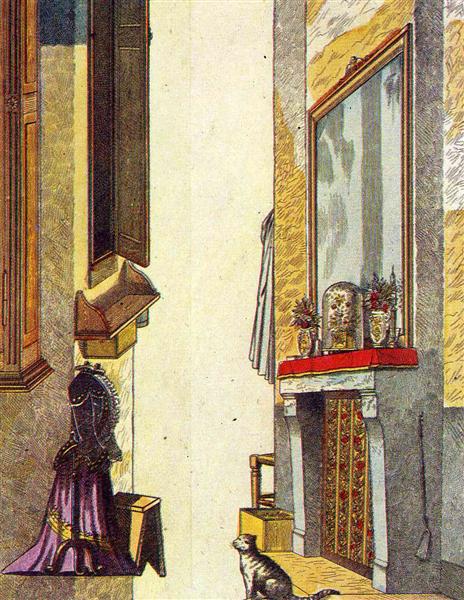
A Legacy of Innovation

Challenging Perceptions

An Enigmatic Artist
Lesson Details & Resources
In a Nutshell
- Artist: Max Ernst
- Year: 1923
- Medium: Oil on canvas
- Location: Museum of Modern Art, New York City
Vocabulary List
- Surrealism
- Max Ernst was a leading figure in the Surrealist movement, known for his dreamlike and fantastical artworks.
- Frottage
- Ernst developed the technique of frottage, which involved rubbing pencil or other materials over a textured surface to create unique patterns and shapes in his artwork.
- Grattage
- He also experimented with grattage, a technique in which he scraped wet paint across a canvas to create unpredictable textures and forms.
- Collage
- Ernst was known for his collage work, where he combined different images and materials to create surreal and thought-provoking compositions.
- Automatic drawing
- He often used the technique of automatic drawing, allowing his hand to move freely across the paper without conscious control, resulting in spontaneous and abstract imagery.
- Surrealist automatism
- Ernst was a proponent of Surrealist automatism, a method in which artists tapped into their unconscious mind to create art without rational thought.
- Bird-headed creatures
- One of Ernst's recurring motifs in his artwork was the inclusion of bird-headed creatures, which symbolized the merging of human and animal forms.
- Landscape of the mind
- Ernst's strange, otherworldly landscapes were often seen as representations of the inner workings of the human psyche.
- Dreamlike
- His artwork often had a dreamlike quality, with fantastical imagery and surreal compositions that defied traditional logic.
- Absurdity
- Ernst's work was characterized by a sense of absurdity and irrationality, challenging viewers to question their perceptions of reality.
- Symbolism
- He used symbolic imagery in his artwork to convey deeper meanings and explore themes of the unconscious mind.
- Psychological
- Ernst's art was deeply psychological, delving into the subconscious and exploring the complexities of the human psyche.
- Texture
- His use of frottage and grattage techniques created rich textures in his artwork, adding depth and complexity to his compositions.
- Juxtaposition
- Ernst often juxtaposed disparate elements in his collages, creating unexpected and thought-provoking combinations.
- Surreal landscapes
- His surreal landscapes were filled with bizarre and fantastical elements, blurring the line between reality and imagination.
- Dreamscapes
- Ernst's artworks were like dreamscapes, inviting viewers into a world of strange and mysterious imagery.
- Psychoanalytic theory
- His work was influenced by psychoanalytic theory, particularly the ideas of Sigmund Freud, exploring the depths of the unconscious mind.
- Metamorphosis
- Ernst often depicted metamorphosis in his artwork, showing figures and forms transforming and changing into new and unexpected shapes.
- Surrealistic imagery
- His use of surrealistic imagery challenged traditional notions of reality, pushing the boundaries of what art could be.
- Unconscious mind
- Ernst's art delved into the depths of the unconscious mind, exploring hidden desires, fears, and fantasies through his surreal compositions.
Timeline of Max Ernst: An Analysis
Max Ernst is born in Brühl, Germany
Ernst studies philosophy at the University of Bonn
Ernst serves in the German army during World War I
Ernst meets artist Hans Arp and joins the Dada movement in Cologne
Ernst participates in the first Dada exhibition in Paris
Ernst experiments with frottage technique, creating texture by rubbing pencil on paper
Ernst publishes 'Beyond Painting' manifesto
Ernst moves to the United States to escape World War II
Ernst becomes a founding member of the Art of This Century gallery in New York
Ernst collaborates with architect Frederick Kiesler on the design of a surrealist exhibition
Ernst returns to Europe and settles in France
Ernst receives the Grand Prize for Painting at the Venice Biennale
Ernst's work is featured in a retrospective exhibition at the Museum of Modern Art in New York
Ernst dies in Paris, France
Key Facts
This is the information used in the fact matching game
- Max Ernst was a German painter, sculptor, graphic artist, and poet.
- Ernst was a key figure in the Dada and Surrealist movements.
- He invented the technique of frottage, which involves rubbing pencil or crayon on paper over a textured surface to create random patterns.
- Ernst also developed the technique of grattage, in which paint is scraped across canvas to create textured effects.
- His art often featured strange and dreamlike landscapes populated by bizarre creatures.
- Ernst's work often explored themes of the unconscious mind and the juxtaposition of unrelated elements.
- He was deeply influenced by the theories of Sigmund Freud and Carl Jung.
- Ernst's work was banned by the Nazis, who deemed it 'degenerate art'.
- He fled to the United States during World War II and became a prominent figure in the American art scene.
- Ernst's art often featured elements of collage, combining different images and textures to create a new whole.
- He was married to fellow Surrealist artist Dorothea Tanning.
- Ernst's work influenced many later artists, including Jackson Pollock and Arshile Gorky.
- He believed that art should be spontaneous and free from conscious control.
- Ernst's work often featured bird-like creatures, which he called 'Loplop'.
- He was a member of the Paris Surrealist group in the 1920s.
- Ernst's work was deeply influenced by his experiences in World War I, which he saw as a traumatic and senseless conflict.
- He experimented with automatic drawing, a technique in which the hand is allowed to move freely across the paper without conscious control.
- Ernst's art often featured distorted figures and landscapes, reflecting his interest in the uncanny and the surreal.
- He was a prolific writer as well as an artist, publishing several volumes of poetry and essays.
- Ernst's work is known for its innovative use of materials and techniques, pushing the boundaries of traditional art forms.
Analysis & Significance
Artistic Innovation
Max Ernst’s use of frottage and grattage techniques in his artwork introduced a new way of creating surreal, dreamlike imagery. By incorporating chance and spontaneity into his process, Ernst pushed the boundaries of traditional painting methods and embraced the subconscious as a source of inspiration.
Influence on Art History
Ernst’s innovative approach to art paved the way for the Surrealist movement, influencing artists like Salvador Dalí and Joan Miró. His exploration of the unconscious mind and the dream world challenged conventional notions of reality and representation, leading to a new understanding of the role of art in exploring the depths of human experience.
Cultural Significance Today
Today, Max Ernst’s work continues to captivate audiences with its enigmatic and provocative imagery. His unique blend of fantasy, symbolism, and abstraction has solidified his reputation as a master of Surrealist art. His influence can be seen in contemporary art practices, as artists continue to draw inspiration from his groundbreaking techniques and themes.
Max Ernst: An Analysis Games
Take Your Learning Offline
Want a convenient, print-ready study guide for this lesson? Become a Memory Wizards Pro member to unlock the downloadable " Memory Scrolls" for this topic and our entire library!
- ✓ Complete Vocabulary Lists
- ✓ Key Facts & Timelines
- ✓ Beautifully Formatted for Print & Mobile




