Summary of the Punic Wars
Uncover the ancient clashes that shaped the fate of empires.
How Do You Learn Best?
Learn by Listening
Start with the 3-minute audio summary to get the key facts and narrative highlights quickly.
Learn by Reading
Immerse yourself in the 10-minute visual lesson for a comprehensive understanding of the topic.
Learn by Reviewing
Jump directly to the key facts, timeline, and vocabulary lists to build a solid foundation of details.
Learn by Doing
Challenge yourself! Jump straight into the interactive games to learn by trial, error, and discovery.
Audio Library
As one of our featured lessons, this topic includes premium audio guides.
Unlock the Wizard's Cram Session
This powerful audio study guide is a Pro-exclusive feature. Upgrade to Memory Wizards Pro to access this and all of our premium learning tools.
Upgrade to Prothe Punic Wars in 10 Minutes

Introduction
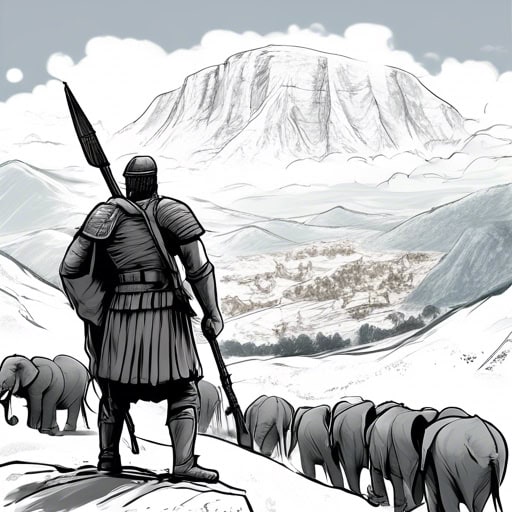


Hannibal Barca

Scipio Africanus

Publius Cornelius Scipio

Hasdrubal Barca

Quintus Fabius Maximus

The First Punic War (264-241 BC)

The Second Punic War (218-201 BC)

The Battle of Cannae (216 BC)

The Siege of Syracuse (214-212 BC)

The Battle of Zama (202 BC)

The Third Punic War (149-146 BC)

Lesson Details & Resources
In a Nutshell
- What: A series of three wars fought between Rome and Carthage for control of the western Mediterranean.
- When: 264-146 BC
- Who: Rome, Carthage, led by prominent figures such as Hannibal Barca
- Outcome: Rome emerged as the dominant power in the Mediterranean, leading to the eventual destruction of Carthage.
Famous Figures in the the Punic Wars
-
Roman general
A highly skilled military leader who played a crucial role in the victories of the Roman Republic during the Punic Wars.
-
Carthaginian general
A strategic military commander of Carthage who led several successful campaigns against the Romans and posed a significant threat to their control.
-
Roman senator
A powerful and influential politician in the Roman Republic who played a vital role in shaping the policies and strategies during the Punic Wars.
-
Carthaginian statesman
A prominent Carthaginian statesman who negotiated treaties and alliances to strengthen Carthage's position in the Punic Wars.
-
Roman consul
A Roman consul who served as one of the highest-ranking officials in the Roman Republic and led armies against the Carthaginians.
-
Carthaginian admiral
A skilled Carthaginian admiral who commanded the powerful Carthaginian navy and sought to gain naval superiority during the Punic Wars.
-
Roman historian
A renowned Roman historian who documented the events and strategies of the Punic Wars, providing valuable insights into the conflict.
-
Carthaginian mercenary
A Carthaginian mercenary who fought for both Carthage and Rome during the Punic Wars, showcasing his skills as a versatile warrior.
-
Roman politician
A Roman politician who played a significant role in the Roman Republic's decision-making process and the formulation of strategies against Carthage.
-
Carthaginian general
A brilliant Carthaginian general who devised innovative tactics and strategies to challenge the Roman forces in the Punic Wars.
Timeline of the Punic Wars
First Punic War begins
Battle of Agrigentum
Battle of Mylae
Battle of Sulci
Battle of Tyndaris
Battle of Cape Ecnomus
Battle of Drepana
Battle of Phintias
Rome captures Agrigentum
Battle of the Aegates Islands
First Punic War ends
Mercenary War begins
Mercenary War ends
Hiero II becomes king of Syracuse
Second Punic War begins
Siege of Saguntum
Battle of Trebia
Battle of Lake Trasimene
Battle of Cannae
Battle of Zama
Second Punic War ends
Vocabulary List
- Carthage
- An ancient city-state located in modern-day Tunisia
- Rome
- The capital city of the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire
- Mediterranean
- A large sea bordered by Europe, Africa, and Asia
- Hannibal
- A Carthaginian general famous for his tactics during the Second Punic War
- Scipio Africanus
- A Roman general who defeated Hannibal in the Battle of Zama
- Sicily
- The largest island in the Mediterranean, which was a major battleground during the Punic Wars
- Elephants
- Large mammals used as weapons by Carthaginian armies, particularly by Hannibal
- Legions
- Large units of Roman soldiers, usually consisting of around 5,000 men
- Naval
- Related to or involving ships or the sea
- Alliances
- Formal agreements between two or more parties to work together towards a common goal
- Siege
- A military tactic where an army surrounds a city or fort in order to cut off supplies and force surrender
- Treaty
- A formal agreement or contract between two or more parties
- Mercenaries
- Hired soldiers who fight for a foreign nation for pay
- Triremes
- Ancient Greek and Roman warships with three rows of oars on each side
- Conquest
- The act of gaining control over a territory through military force
- Senate
- The governing body of the Roman Republic, composed of elected officials
- Battlefield
- The area or location where a battle takes place
- Blockade
- The act of preventing goods or people from entering or leaving a certain area, often by ships or troops
- Warfare
- The activities and strategies involved in fighting a war
- Annihilation
- Complete destruction or obliteration.
Key Facts
This is the information used in the fact matching game
- The Punic Wars were a series of conflicts between Rome and Carthage
- The wars were named after the Latin word for Phoenician, "Punic"
- The First Punic War lasted from 264 BC to 241 BC
- It began due to a dispute over the island of Sicily
- Rome emerged victorious in the First Punic War
- The Second Punic War lasted from 218 BC to 201 BC
- Hannibal Barca was the Carthaginian general who famously crossed the Alps with his army and won several battles against Rome
- Hannibal's most famous victory was the Battle of Cannae in 216 BC
- Scipio Africanus was the Roman general who ultimately defeated Hannibal at the Battle of Zama in 202 BC
- The Third Punic War took place from 149 BC to 146 BC
- Carthage was completely destroyed by the Romans at the end of the Third Punic War
- The Punic Wars were primarily fought over control of the Mediterranean Sea
- The wars established Rome as the dominant power in the Mediterranean region
- The Punic Wars saw the use of various military tactics and innovations, such as the corvus, a boarding device used by Roman ships
- The wars also witnessed the use of war elephants by the Carthaginians
- The First Punic War was mainly fought at sea, while the Second Punic War involved land battles as well
- The Punic Wars resulted in significant loss of life and resources for both Rome and Carthage
- The wars had a profound impact on the Roman Republic, leading to changes in military strategy, expansion, and political power
- The Punic Wars marked the beginning of Rome's imperialistic ambitions
- The conflicts between Rome and Carthage were fueled by long-standing grievances and a desire for dominance in the Mediterranean.
Analysis & Significance
Immediate Consequences
The Punic Wars, spanning over a century, resulted in the destruction of Carthage, a once powerful city-state in North Africa, and the expansion of Roman territory and influence in the Mediterranean. The wars also led to the rise of Rome as the dominant power in the region, solidifying its position as a major empire.
Long-Term Impact
The aftermath of the Punic Wars had a profound impact on the course of history. The defeat of Carthage marked the end of the Phoenician civilization in the Mediterranean and paved the way for Roman domination of the region. The wars also established Rome as the preeminent power in the ancient world, setting the stage for its eventual transformation into a vast empire.
Cultural Significance Today
The legacy of the Punic Wars can still be felt today in the form of cultural influences and historical significance. The conflicts between Rome and Carthage continue to be studied as a pivotal moment in ancient history, shaping the development of Western civilization. The wars also serve as a reminder of the consequences of imperial ambition and the impact of military conquest on societies and cultures.
the Punic Wars Games
Take Your Learning Offline
Want a convenient, print-ready study guide for this lesson? Become a Memory Wizards Pro member to unlock the downloadable " Memory Scrolls" for this topic and our entire library!
- ✓ Complete Vocabulary Lists
- ✓ Key Facts & Timelines
- ✓ Beautifully Formatted for Print & Mobile




