Diocletian: A Military and Administrative Biography
The formidable emperor who divided the Roman Empire and restored order.
How Do You Learn Best?
Learn by Reading
Immerse yourself in the 10-minute visual lesson for a comprehensive understanding of the topic.
Learn by Reviewing
Jump directly to the key facts, timeline, and vocabulary lists to build a solid foundation of details.
Learn by Doing
Challenge yourself! Jump straight into the interactive games to learn by trial, error, and discovery.
Diocletian: A Military and Administrative Biography in 10 Minutes

Introduction



Maximian

Galerius

Constantine the Great

Rise to Power
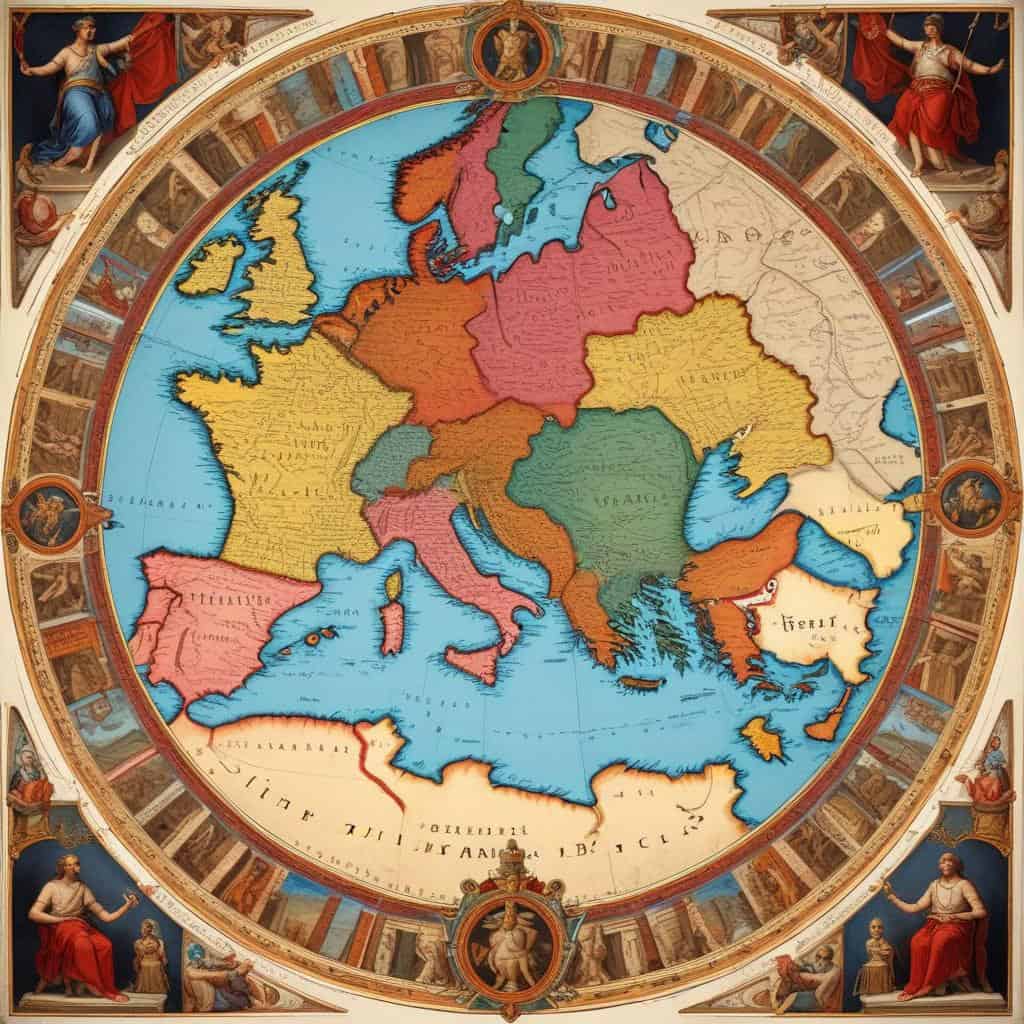
Tetrarchy

Economic Reforms

Persecution of Christians

Retirement

Death

Legacy

Impact on Roman Empire

Historical Significance

Remembering Diocletian
Lesson Details & Resources
In a Nutshell
- Who: Roman Emperor and founder of the Tetrarchy
- When: Lived: 244 – 311 AD
- Known For: Instituting economic and political reforms in the Roman Empire
- Legacy: Splitting the empire into East and West, setting the stage for the Byzantine Empire
Timeline of Diocletian: A Military and Administrative Biography
Diocletian is born in Salona, Dalmatia
Diocletian is proclaimed emperor by the army in Nicomedia
Diocletian appoints Maximian as co-emperor in Milan
Diocletian defeats Carinus at the Battle of the Margus River
Diocletian reforms the Roman currency, introducing the argenteus and aureus coins
Diocletian divides the Roman Empire into the Western and Eastern regions
Diocletian begins persecuting Christians, initiating the Diocletianic Persecution
Diocletian abdicates the throne in favor of Maximian and Constantius Chlorus
Diocletian retires to his palace in Split, Croatia (Spalatum)
Diocletian dies in Split, Croatia
Vocabulary List
- Tetrarchy
- Diocletian's division of the Roman Empire into four separate territories ruled by two senior emperors and two junior emperors.
- Edict on Maximum Prices
- A decree issued by Diocletian in 301 AD that set maximum prices for goods and services in an attempt to stabilize the economy.
- Persecution of Christians
- Diocletian's campaign against Christians, which included the destruction of churches and the execution of believers.
- Abdication
- Diocletian's decision to retire from the position of emperor in 305 AD, leading to a period of instability in the Roman Empire.
- Augustus
- The title given to Diocletian as one of the senior emperors in the Tetrarchy system.
Key Facts
This is the information used in the fact matching game
- Diocletian was a Roman emperor who ruled from 284 to 305 AD.
- He is best known for his reforms that divided the Roman Empire into the Western and Eastern halves.
- Diocletian was born in 244 AD in Dalmatia, which is now modern-day Croatia.
- He rose through the ranks of the Roman military to become emperor in 284 AD.
- Diocletian was the first emperor to voluntarily abdicate the throne in 305 AD.
- He implemented a series of economic reforms to stabilize the Roman economy.
- Diocletian persecuted Christians during his reign, leading to the Diocletianic Persecution.
- He built the massive palace complex of Split in Croatia as his retirement home.
- Diocletian's reforms included the establishment of the Tetrarchy, a system of four co-emperors ruling different regions of the empire.
- He attempted to combat inflation by introducing a new currency system known as the Edict on Maximum Prices.
- Diocletian is credited with strengthening the borders of the Roman Empire through military campaigns and fortifications.
- He was known for his authoritarian rule and strict enforcement of laws and regulations.
- Diocletian's reign marked the end of the Crisis of the Third Century in the Roman Empire.
- He was the first Roman emperor to be addressed as dominus et deus, meaning 'lord and god.'
- Diocletian retired to his palace in Split in 305 AD and lived out the remainder of his life in seclusion.
- He died in 311 AD and was deified by his successors.
- Diocletian's reforms laid the foundation for the Byzantine Empire, which would last for nearly a thousand years after the fall of Rome.
- He is considered one of the most influential emperors in Roman history.
- Diocletian's legacy is a complex one, with some praising his reforms and others condemning his persecution of Christians.
- He is often depicted in art and literature as a powerful and imposing figure, reflecting his reputation as a strong and effective ruler.
Analysis & Significance
Major Accomplishments
Diocletian, a Roman emperor, is best known for his administrative reforms known as the Tetrarchy, which divided the Roman Empire into Eastern and Western regions. He also implemented price controls to stabilize the economy and initiated the largest Roman persecution of Christians.
Impact on the World
Diocletian’s reforms transformed the Roman Empire, setting the stage for the Byzantine Empire and shaping the political structure for centuries to come. His persecution of Christians had a significant impact on the spread and development of Christianity, leading to martyrdom and the eventual legalization of the religion.
Enduring Legacy
Today, Diocletian is remembered as a pivotal figure in Roman history, known for his authoritarian rule and lasting impact on the empire’s structure. His administrative reforms and persecution of Christians continue to be studied by historians, shedding light on the complexities of governance and religious freedom in ancient Rome.
Diocletian: A Military and Administrative Biography Games
Take Your Learning Offline
Want a convenient, print-ready study guide for this lesson? Become a Memory Wizards Pro member to unlock the downloadable " Memory Scrolls" for this topic and our entire library!
- ✓ Complete Vocabulary Lists
- ✓ Key Facts & Timelines
- ✓ Beautifully Formatted for Print & Mobile




