Summary of Roman Withdrawal from Britain
Uncover the mystery behind Rome's departure from ancient Britannia.
How Do You Learn Best?
Learn by Reading
Immerse yourself in the 10-minute visual lesson for a comprehensive understanding of the topic.
Learn by Reviewing
Jump directly to the key facts, timeline, and vocabulary lists to build a solid foundation of details.
Learn by Doing
Challenge yourself! Jump straight into the interactive games to learn by trial, error, and discovery.
Roman Withdrawal from Britain in 10 Minutes

Introduction



Emperor Honorius

Stilicho

Barbarian Invaders

Roman Legions in Britain
British Tribes

The Roman Occupation of Britain

The Decline of Roman Power
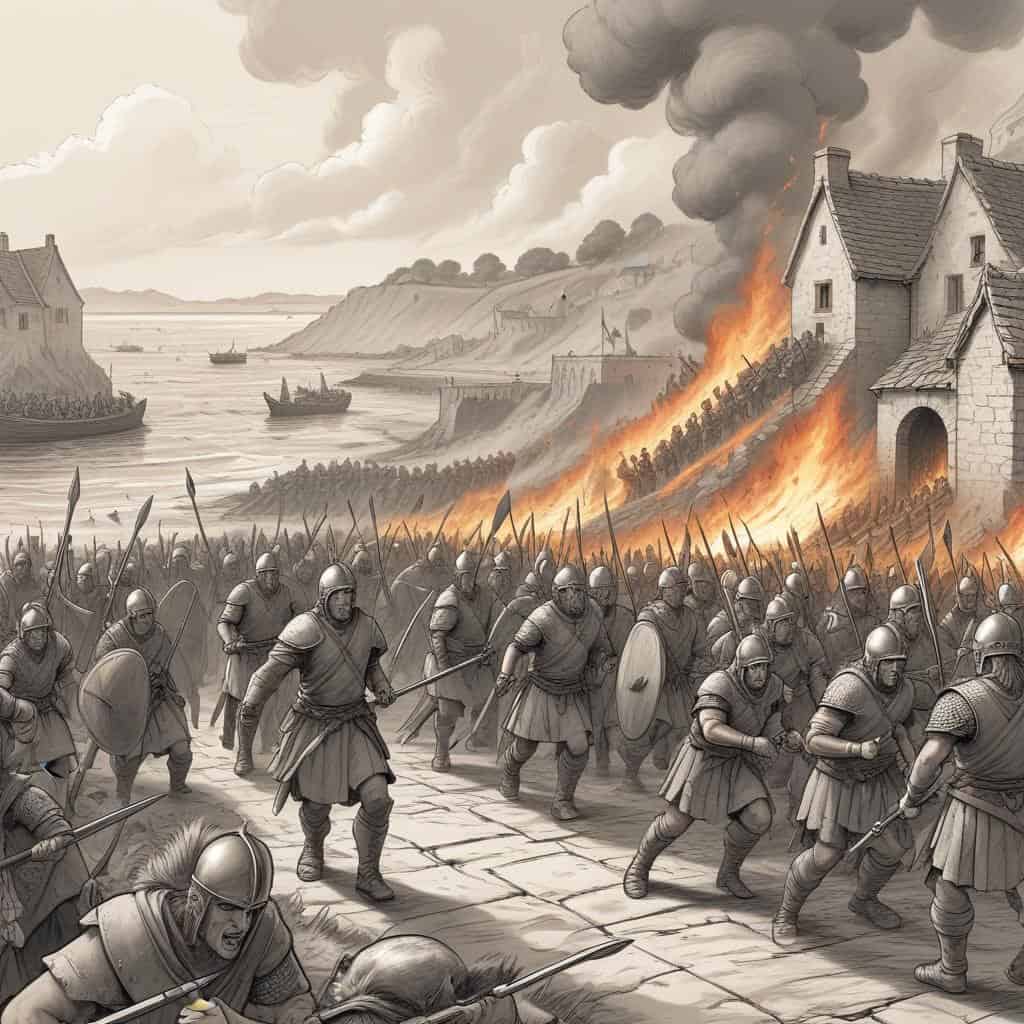

The Saxon Raids

The Revolt of Constantine III

The Roman Withdrawal

The Power Vacuum
The Rise of the Anglo-Saxons

The Legacy of Roman Britain

The Fall of Rome

The End of an Era

Lesson Details & Resources
In a Nutshell
- What: The Roman Withdrawal from Britain (410 AD)
- When: 410 AD
- Who: Romans, Britons
- Outcome: Beginning of the end of Roman rule in Britain
Famous Figures in the Roman Withdrawal from Britain
-
Honorius
Honorius: Honorius was the Roman Emperor at the time of the withdrawal from Britain. He was known for his weak leadership and inability to effectively counter the threats faced by the Roman Empire.
-
Alaric I
Alaric I: Alaric I was the Visigothic king who led the sack of Rome in 410 AD, an event often seen as one of the triggers for the Roman withdrawal from Britain.
-
Constantine III
Constantine III: Constantine III was a Roman general who declared himself emperor in Britain in 407 AD. His short-lived rule marked a period of turmoil and contributed to the weakening of Roman control in Britain.
-
Romulus Augustus
Romulus Augustus: Romulus Augustus, also known as Augustulus, was the last Roman emperor before the deposition of the Western Roman Empire in 476 AD. Although not directly related to the withdrawal from Britain, his reign symbolizes the decline and fall of the Roman Empire.
-
Stilicho
Stilicho: Flavius Stilicho was a Vandal serving as a general of the Western Roman Empire. He played a significant role in defending Britain against invading forces and maintaining Roman control until his execution in 408 AD.
Timeline of Roman Withdrawal from Britain
Emperor Honorius sends a letter to the Romano-British cities, informing them that they must fend for themselves
Roman troops are withdrawn from Hadrian's Wall
Saxon raids intensify along the east coast of Britain
Roman administration collapses in Britain
Romano-British cities struggle to defend themselves against invading tribes
Celtic tribes such as the Picts and Scots take advantage of the Roman withdrawal
Roman presence in Britain diminishes significantly
Romano-British leaders try to negotiate with Germanic tribes for assistance
Germanic tribes, including the Angles, Saxons, and Jutes, begin to settle in Britain
Germanic tribes establish their own kingdoms in Britain
Romano-British society gradually adopts Germanic customs and languages
Romano-British art, architecture, and culture experience a decline
Roman influence in Britain becomes limited to the Church
The Romano-British leader Vortigern invites the Saxons to fight against the Picts and Scots
The Saxons, now settled in Britain, turn against the Romano-British and begin their own conquest
The Romano-British leader Ambrosius Aurelianus leads resistance against the Saxons
Arthur, a legendary Romano-British leader, emerges as a symbol of resistance against the invaders
The Anglo-Saxon kingdoms establish dominance over most of Britain
The period known as the Dark Ages begins in Britain
Roman influence in Britain is limited to remnants of Roman architecture and infrastructure
Vocabulary List
- Roman
- The Roman Empire was a powerful civilization that dominated much of Europe, including Britain, for several centuries.
- Withdrawal
- The withdrawal of Roman forces from Britain in 410 AD marked the end of Roman rule in the island.
- Britain
- Britain, also known as Britannia, was a province of the Roman Empire from 43 AD until the Roman withdrawal in 410 AD.
- 410 AD
- In 410 AD, the Roman Emperor Honorius ordered the withdrawal of Roman legions from Britain, leaving the island vulnerable to invasions.
- Roman Empire
- The Roman Empire was a vast and powerful state that encompassed various territories, including Britain, during its peak.
- Rule
- Roman rule in Britain brought infrastructure, governance, and cultural influences to the island.
- Civilization
- The Romans were known for their advanced civilization, characterized by achievements in architecture, engineering, law, and military tactics.
- Legions
- Roman legions were well-disciplined and highly trained military units that played a crucial role in maintaining control over the provinces.
- Invasions
- After the Roman withdrawal, Britain experienced numerous invasions by various Germanic tribes, such as the Angles, Saxons, and Jutes.
- Province
- Britain was initially a province of the Roman Empire, governed by a provincial governor appointed by the Emperor.
Key Facts
This is the information used in the fact matching game
- The Roman Emperor Honorius ordered the withdrawal of Roman troops from Britain in 410 AD.
- The Roman withdrawal from Britain marked the end of Roman rule in the island.
- The Roman withdrawal left Britain vulnerable to invasions by Picts, Scots, and Anglo-Saxon tribes.
- The Roman legions stationed in Britain were mostly recalled to defend the weakening Roman Empire.
- The withdrawal was part of a larger collapse of Roman authority in Western Europe.
- The Roman withdrawal from Britain was not an immediate abandonment, but a gradual process over several decades.
- The Roman withdrawal had a significant impact on the economy and infrastructure of Britain.
- Without Roman protection, local Britons had to form their own defenses against invasions.
- The withdrawal led to increased power and influence of local British leaders.
- The Roman withdrawal contributed to the fragmentation of Britain into multiple smaller kingdoms.
- The withdrawal allowed the spread of Christianity to flourish in Britain.
- The Roman withdrawal created a power vacuum that was later filled by the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms.
- The withdrawal led to the decline of urban centers in Britain as Roman infrastructure crumbled.
- The Roman withdrawal had a lasting impact on the culture and language of Britain.
- The withdrawal marked the beginning of the Dark Ages in Britain.
- Some Roman-British elites sought alliances with Germanic tribes to maintain their power after the withdrawal.
- The Roman withdrawal allowed the development of distinct regional identities in Britain.
- The withdrawal made Britain more vulnerable to raids by Viking pirates in the following centuries.
- The Roman withdrawal from Britain is often considered a turning point in British history.
- The withdrawal left a lasting legacy of Roman influence in Britain, including in laws and governance.
Analysis & Significance
Immediate Consequences
The Roman withdrawal from Britain in 410 AD left the island vulnerable to invasions from the Saxons, Angles, and Jutes, leading to a period of instability and conflict as native Britons struggled to defend their lands.
Long-Term Impact
The Roman withdrawal marked the end of Roman rule in Britain and the beginning of the Dark Ages in the region. It also paved the way for the Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, shaping the future of the island’s culture and history.
Cultural Significance Today
The Roman withdrawal from Britain continues to be a topic of historical study and debate, with its legacy influencing the development of British identity and national pride. The event serves as a reminder of the importance of strong leadership and defense in maintaining a stable society.
Roman Withdrawal from Britain Games
Take Your Learning Offline
Want a convenient, print-ready study guide for this lesson? Become a Memory Wizards Pro member to unlock the downloadable " Memory Scrolls" for this topic and our entire library!
- ✓ Complete Vocabulary Lists
- ✓ Key Facts & Timelines
- ✓ Beautifully Formatted for Print & Mobile




