Summary of The Unification of China (221 BCE)
Discover the legendary emperor who united a fractured land in ancient China.
How Do You Learn Best?
Learn by Reading
Immerse yourself in the 10-minute visual lesson for a comprehensive understanding of the topic.
Learn by Reviewing
Jump directly to the key facts, timeline, and vocabulary lists to build a solid foundation of details.
Learn by Doing
Challenge yourself! Jump straight into the interactive games to learn by trial, error, and discovery.
The Unification of China in 10 Minutes

Introduction


Qin Shi Huang

Li Si

Xiang Yu

Liu Bang

The Rise of the Qin Dynasty

The Standardization of Laws and Writing

The Construction of the Great Wall
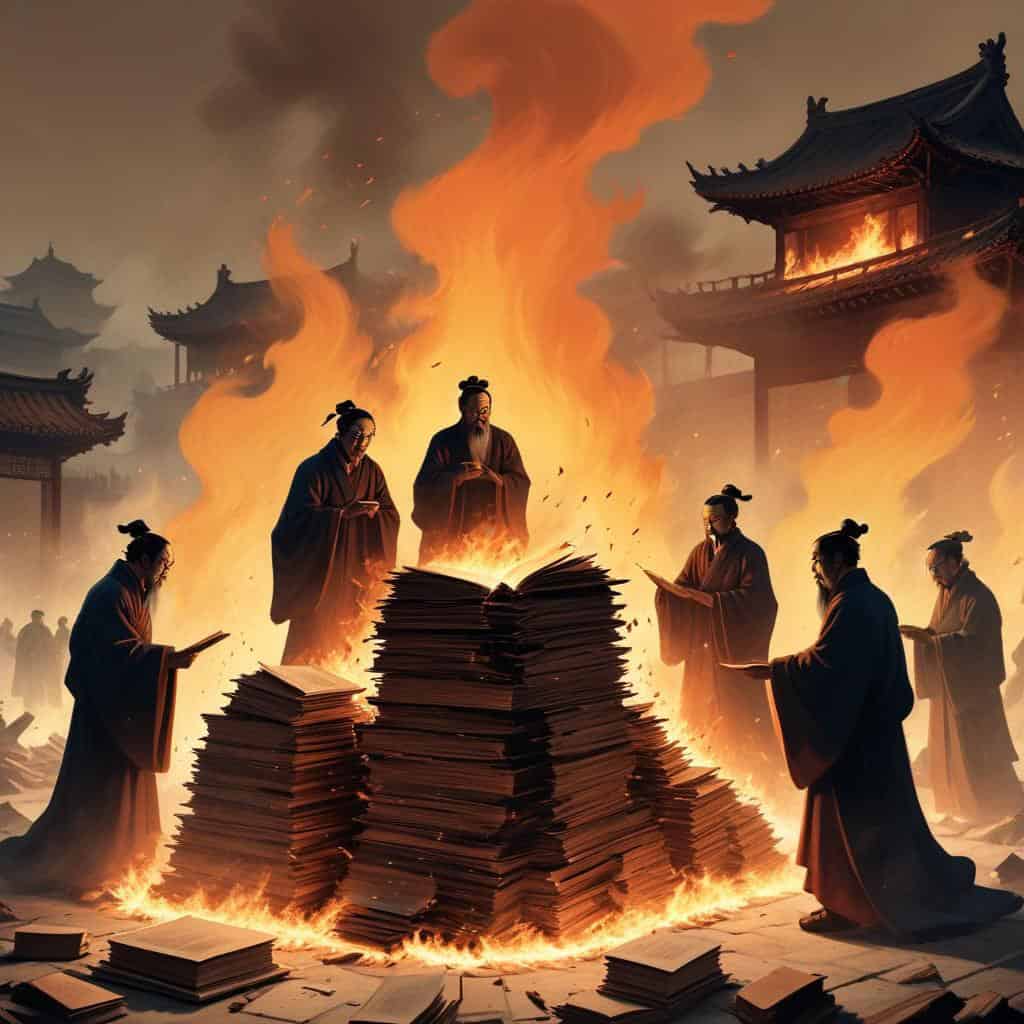

The Burning of Books and Confucian Scholars

The Fall of the Qin Dynasty

The Rise of the Han Dynasty

The Adoption of Confucianism

The Expansion of the Silk Road

The Invention of Paper and the Compass

The Legacy of Chinas Unification

Lesson Details & Resources
In a Nutshell
- What: The unification of China under the Qin Dynasty.
- When: 221 BCE
- Who: Qin Shi Huang, the first emperor of China.
- Outcome: Establishment of a centralized imperial government, standardized currency, weights, and measures, and the beginning of the Great Wall of China construction.
Famous Figures in the The Unification of China
-
Qin Shi Huang
Qin Shi Huang was the first emperor of China and is known for unifying China and standardizing various aspects of Chinese society.
-
Li Si
Li Si was a prominent politician and advisor to Qin Shi Huang, playing a key role in the unification of China.
-
Zhao Gao
Zhao Gao was a powerful eunuch who played a significant role in the downfall of the Qin dynasty after the unification of China.
-
Xiang Yu
Xiang Yu was a military leader who fought against the Qin dynasty during the Chu–Han Contention period following the unification of China.
-
Liu Bang
Liu Bang was the founder of the Han dynasty and played a key role in overthrowing the Qin dynasty and unifying China.
Timeline of The Unification of China
Qin Dynasty conquers the six other states of China
Qin Shi Huang becomes the first Emperor of China
Standardization of writing, weights, and measures
Construction of the Great Wall of China begins
Burning of books and burying of scholars
Death of Qin Shi Huang
Rebellion against the Qin Dynasty begins
Fall of the Qin Dynasty
Liu Bang establishes the Han Dynasty
End of the Warring States period
Establishment of centralized bureaucratic government
Expansion of the Chinese empire
Confucianism becomes the official state ideology
Silk Road trade route established
Introduction of civil service exams
Reign of Emperor Wu of Han
Establishment of the Silk Road trade route
Introduction of paper making
End of the Han Dynasty
Beginning of the Three Kingdoms period
Vocabulary List
- Qin Dynasty
- The Qin Dynasty was the ruling dynasty during the time of the unification of China in 221 BCE.
- Legalism
- Legalism was the dominant political philosophy of the Qin Dynasty that emphasized strict laws and harsh punishments.
- Great Wall
- The Great Wall of China was built during the Qin Dynasty as a defense against invasions from northern tribes.
- Terracotta Army
- The Terracotta Army was created during the Qin Dynasty to protect the first Qin emperor in the afterlife.
- Emperor Qin Shi Huang
- Emperor Qin Shi Huang was the first emperor of China and the one who unified the country in 221 BCE.
Key Facts
This is the information used in the fact matching game
- The Unification of China in 221 BCE marked the end of the Warring States period.
- The unification was achieved by the Qin Dynasty under the leadership of Qin Shi Huang.
- Qin Shi Huang proclaimed himself the first emperor of China after the unification.
- The unification involved the conquest and annexation of the other six major states in China.
- The unification brought about a centralized government and standardized laws and systems.
- Qin Shi Huang implemented a series of reforms to strengthen the newly unified empire.
- The unification led to the standardization of writing, currency, and measurements in China.
- Qin Shi Huang ordered the construction of the Great Wall of China as a defense against invasions.
- The unification of China laid the foundation for the subsequent Han Dynasty.
- Qin Shi Huang's reign was marked by authoritarian rule and harsh policies.
- The unification of China brought about significant cultural and societal changes.
- Qin Shi Huang's mausoleum is famous for the terracotta army found buried with him.
- The unification of China expanded the empire's territory and influence.
- Qin Shi Huang's reign saw the standardization of weights and measures throughout China.
- The unification of China brought about the abolishment of feudalism and the establishment of a centralized government.
- Qin Shi Huang's policies and actions were aimed at consolidating power and control over the empire.
- The unification of China paved the way for the development of a unified Chinese identity.
- Qin Shi Huang's reign saw the construction of the Qin Imperial Palace, a grand complex in Xianyang.
- The unification of China brought about the standardization of the Chinese script, which helped facilitate communication and administration.
- Qin Shi Huang's policies and reforms had a lasting impact on Chinese history and culture.
Analysis & Significance
Immediate Consequences
The unification of China in 221 BCE under the Qin Dynasty brought about a centralized government, standardization of measurements, currency, and writing system. It also led to the construction of the Great Wall of China to protect against invasions from the north.
Long-Term Impact
This event laid the foundation for the long-lasting imperial system in China, setting the stage for dynasties such as the Han, Tang, and Ming. The unification also facilitated cultural exchange and economic growth, influencing neighboring regions and shaping Chinese civilization for centuries to come.
Cultural Significance Today
The legacy of the unification of China is still evident in China’s national identity, governance structure, and Confucian values. The Great Wall remains a symbol of China’s strength and resilience, attracting millions of tourists annually. Furthermore, the unification’s impact on language, philosophy, and art continues to shape Chinese culture and influence global perspectives on history and civilization.
The Unification of China Games
Take Your Learning Offline
Want a convenient, print-ready study guide for this lesson? Become a Memory Wizards Pro member to unlock the downloadable " Memory Scrolls" for this topic and our entire library!
- ✓ Complete Vocabulary Lists
- ✓ Key Facts & Timelines
- ✓ Beautifully Formatted for Print & Mobile




