Summary of Kingdom of Axum
Uncover the mysteries of ancient Africa's forgotten empire, the Kingdom of Axum.
How Do You Learn Best?
Learn by Listening
Start with the 3-minute audio summary to get the key facts and narrative highlights quickly.
Learn by Reading
Immerse yourself in the 10-minute visual lesson for a comprehensive understanding of the topic.
Learn by Reviewing
Jump directly to the key facts, timeline, and vocabulary lists to build a solid foundation of details.
Learn by Doing
Challenge yourself! Jump straight into the interactive games to learn by trial, error, and discovery.
Audio Library
As one of our featured lessons, this topic includes premium audio guides.
Unlock the Wizard's Cram Session
This powerful audio study guide is a Pro-exclusive feature. Upgrade to Memory Wizards Pro to access this and all of our premium learning tools.
Upgrade to ProKingdom of Axum in 10 Minutes

Introduction



King Ezana

Queen Gudit

King Kaleb

Queen Makeda

Early Origins
Trade and Prosperity

Christianity

The Obelisks

Queen of Sheba

Decline and Fall

Legacy

Archaeological Discoveries
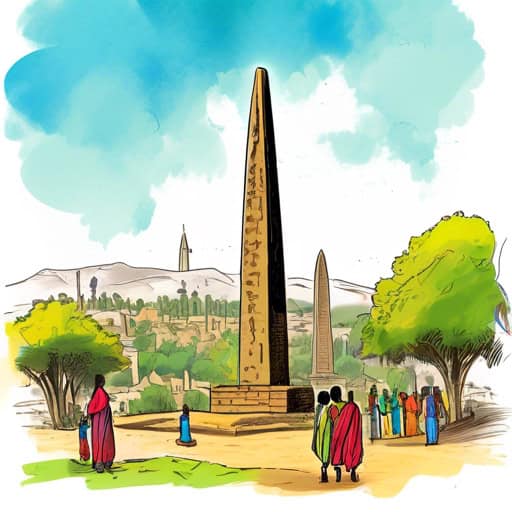

Modern Axum

Lesson Details & Resources
In a Nutshell
- What: An ancient kingdom in East Africa known for its trade and Christianity.
- When: 100 AD – 940 AD
- Who: King Ezana, Queen Gudit, King Kaleb
- Outcome: Established a powerful trade network and became one of the first Christian kingdoms in the world.
Famous Figures in the Kingdom of Axum
-
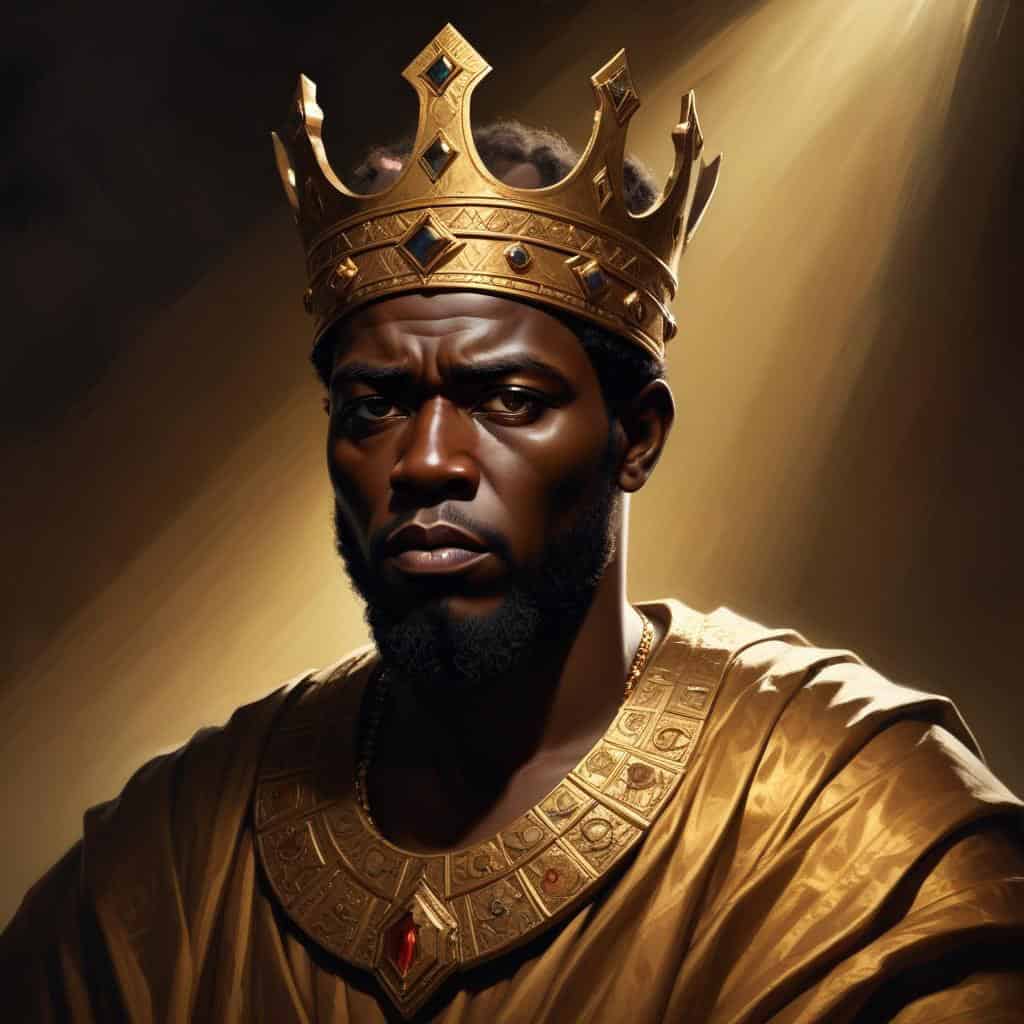

King Ezana
King Ezana was a ruler of the Kingdom of Axum known for converting to Christianity and making it the official religion.
-
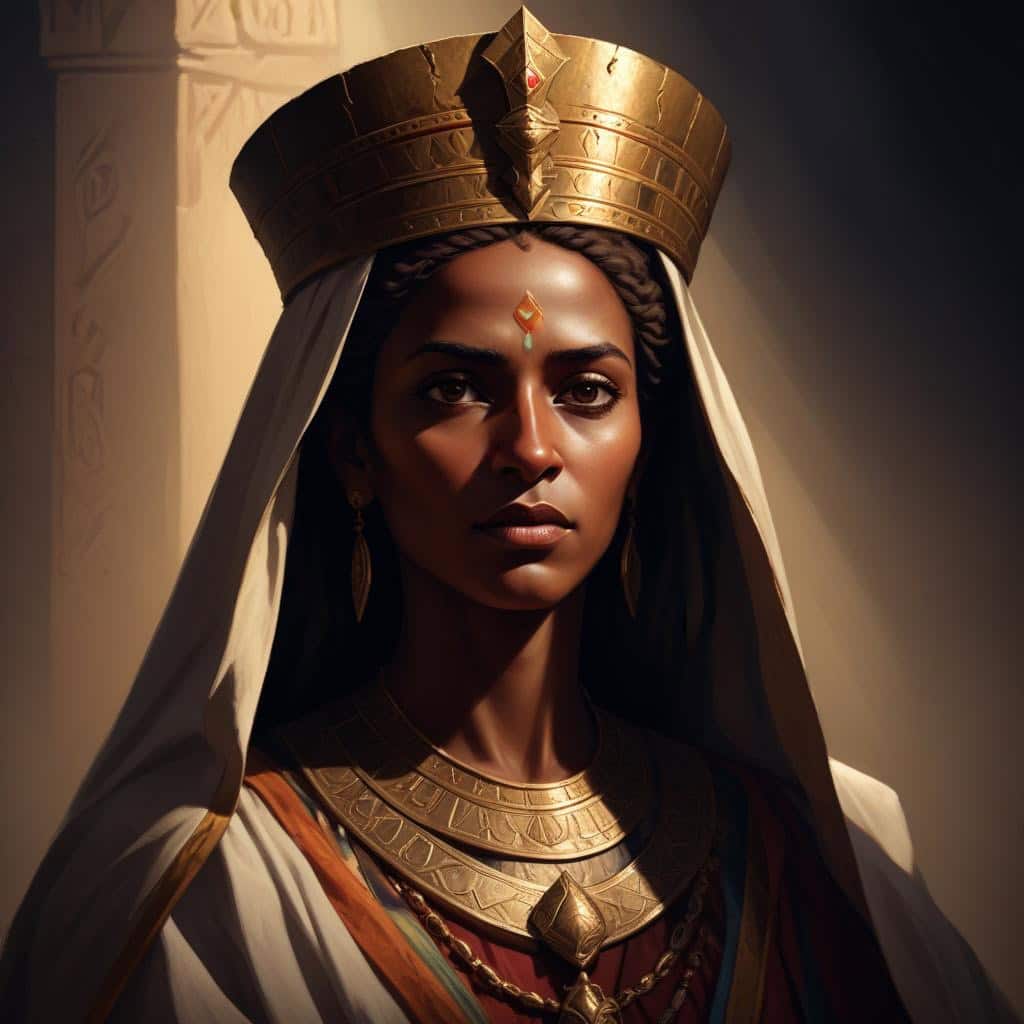

Queen Gudit
Queen Gudit was a legendary queen who is believed to have overthrown the ruling dynasty of Axum in the 10th century.
-

King Kaleb
King Kaleb was a ruler of Axum known for his military campaigns and expansions of the kingdom.
-

King Zoskales
King Zoskales was a ruler of Axum who is mentioned in ancient inscriptions as a powerful king.
-

Queen Yodit
Queen Yodit, also known as Queen Gudit, is believed to have destroyed the Kingdom of Axum in the 10th century.
Timeline of Kingdom of Axum
Kingdom of Axum is founded
Construction of the obelisks in Axum
King Ezana converts to Christianity
Axum becomes a major trading power in the region
Axumite invasion of Kush
Islamic conquest of Axum
Decline of Axum as a political power
Portuguese establish contact with Axum
Axumite civilization rediscovered by European explorers
Italian occupation of Axum
Ethiopian liberation of Axum from Italian occupation
Axum becomes part of Ethiopia
Axum designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site
Discovery of the Ark of the Covenant in Axum
Axumite ruins looted during civil war in Ethiopia
Axumite artifacts returned to Ethiopia
Archaeological excavations reveal more about Axumite civilization
Axum becomes a popular tourist destination
Axumite language and script deciphered by scholars
Vocabulary List
- Aksumite
- The Aksumite Kingdom was an ancient civilization in the region of modern-day Ethiopia and Eritrea.
- Obelisk
- The Kingdom of Axum is known for its large obelisks, which were used as grave markers for important individuals.
- Stelae
- The Kingdom of Axum is also known for its stelae, tall stone pillars that were often inscribed with important information.
- Coinage
- The Kingdom of Axum was one of the first African civilizations to have its own coinage, which helped facilitate trade.
- Red Sea
- The Kingdom of Axum had access to the Red Sea, which allowed for trade with other civilizations in the region.
- Port
- The Kingdom of Axum had a thriving port city called Adulis, which was an important hub for trade in the region.
- Monolithic churches
- The Kingdom of Axum is known for its monolithic churches, which were carved out of solid rock.
- Queen of Sheba
- According to Ethiopian tradition, the Queen of Sheba visited King Solomon in Israel and returned to Axum pregnant with his child.
Key Facts
This is the information used in the fact matching game
- Axum was an ancient kingdom located in present-day Ethiopia and Eritrea.
- Axum was one of the great civilizations of Africa and one of the oldest continuous Christian kingdoms in the world.
- The Kingdom of Axum was a major trading power in the region, with trade routes connecting it to Egypt, Arabia, Persia, India, and the Roman Empire.
- Axum was known for its impressive stone obelisks, some of which were over 100 feet tall.
- The Kingdom of Axum adopted Christianity in the 4th century, making it one of the earliest Christian kingdoms in the world.
- The Axumite Empire was at its height between the 4th and 7th centuries AD.
- Axum was a major center of trade, with goods such as ivory, gold, and spices passing through its ports.
- The Kingdom of Axum minted its own coins, which were used for trade throughout the region.
- Axumite architecture was characterized by large stone buildings, including palaces, temples, and royal tombs.
- The fall of the Kingdom of Axum is attributed to a combination of factors, including the rise of Islam, environmental changes, and invasions by neighboring kingdoms.
- The Kingdom of Axum had a written language known as Ge'ez, which is still used in the Ethiopian Orthodox Church.
- Axum was a monarchy ruled by a series of kings and queens known as neguses and negestis.
- The Kingdom of Axum had a complex system of agriculture, including terraced farming and irrigation.
- Axum was known for its impressive stelae, or carved stone monuments, which were often erected to commemorate rulers or important events.
- The Kingdom of Axum had a strong military, which allowed it to expand its territory and influence in the region.
- Axum was a cosmopolitan society with a diverse population, including Greeks, Arabs, Persians, and Africans.
- The Kingdom of Axum was known for its advanced technology, including the use of iron tools and weapons.
- Axum was a center of arts and culture, with a rich tradition of music, dance, and literature.
- The Kingdom of Axum had a sophisticated system of governance, with laws, courts, and administrative officials.
- Axum was a pioneer in the development of Christianity in Africa, with its own unique form of the religion that blended local traditions with Christian beliefs.
Analysis & Significance
Immediate Consequences
The Kingdom of Axum’s establishment as a major trading power in the ancient world led to increased wealth and prosperity for its people. Its strategic location along trade routes connecting Africa, Arabia, and India brought in valuable goods and resources, boosting the kingdom’s economy and influence in the region.
Long-Term Impact
Axum’s legacy endured long after its decline, leaving behind impressive architectural marvels like the obelisks and churches that still stand today. The kingdom’s conversion to Christianity in the 4th century AD played a significant role in shaping the religious and cultural landscape of Ethiopia, leaving a lasting impact on the country’s identity and traditions.
Cultural Significance Today
The Kingdom of Axum continues to be a source of pride and inspiration for modern Ethiopians, who view it as a symbol of their rich history and heritage. Its influence can be seen in the country’s religious practices, art, and architecture, preserving the memory of this ancient civilization for future generations to appreciate and learn from.
Kingdom of Axum Games
Take Your Learning Offline
Want a convenient, print-ready study guide for this lesson? Become a Memory Wizards Pro member to unlock the downloadable " Memory Scrolls" for this topic and our entire library!
- ✓ Complete Vocabulary Lists
- ✓ Key Facts & Timelines
- ✓ Beautifully Formatted for Print & Mobile




