How Do You Learn Best?
Learn by Listening
Start with the 3-minute audio summary to get the key facts and narrative highlights quickly.
Learn by Reading
Immerse yourself in the 10-minute visual lesson for a comprehensive understanding of the topic.
Learn by Reviewing
Jump directly to the key facts, timeline, and vocabulary lists to build a solid foundation of details.
Learn by Doing
Challenge yourself! Jump straight into the interactive games to learn by trial, error, and discovery.
Example of Post Impressionism: sunday-in-the-park

Deconstructing Post Impressionism
Vivid Color Palette
Bold and expressive use of color enhances emotional depth and creates a sense of vibrancy in the artwork.
Distinct Brushwork
Visible brushstrokes and textured surfaces show the artist's individual style and emphasize the act of painting itself.
Symbolic Imagery
Inclusion of symbolic elements and personal iconography adds layers of meaning and invites interpretation from the viewer.
Audio Library
As one of our featured lessons, this topic includes premium audio guides.
Key Artists of Post-Impressionism: An Analysis in 10 Minutes

Introduction

Vincent van Gogh: A Tormented Genius

Paul Cézanne: The Father of Modern Art
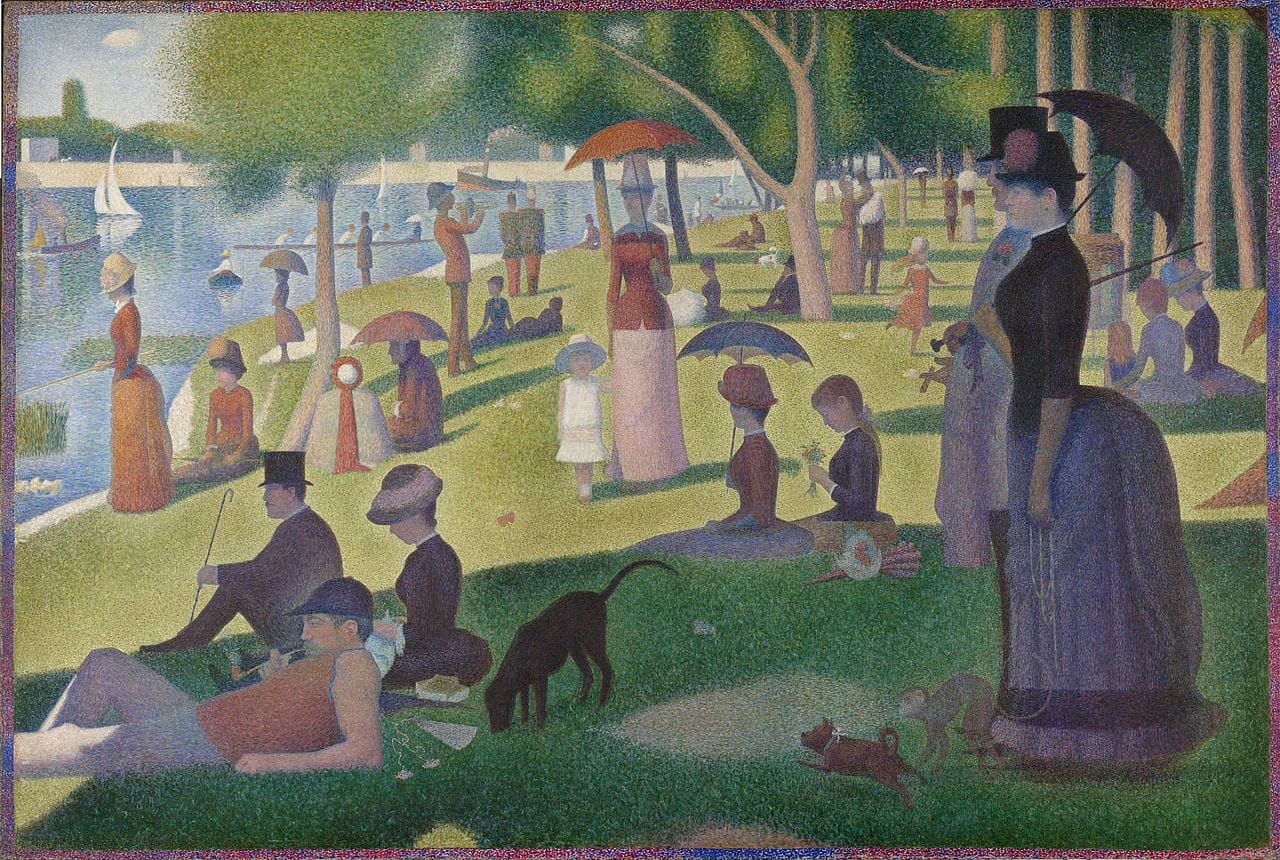
Georges Seurat: The Pointillist Pioneer

Paul Gauguin: A Quest for Paradise

Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec: The Chronicler of Parisian Nightlife
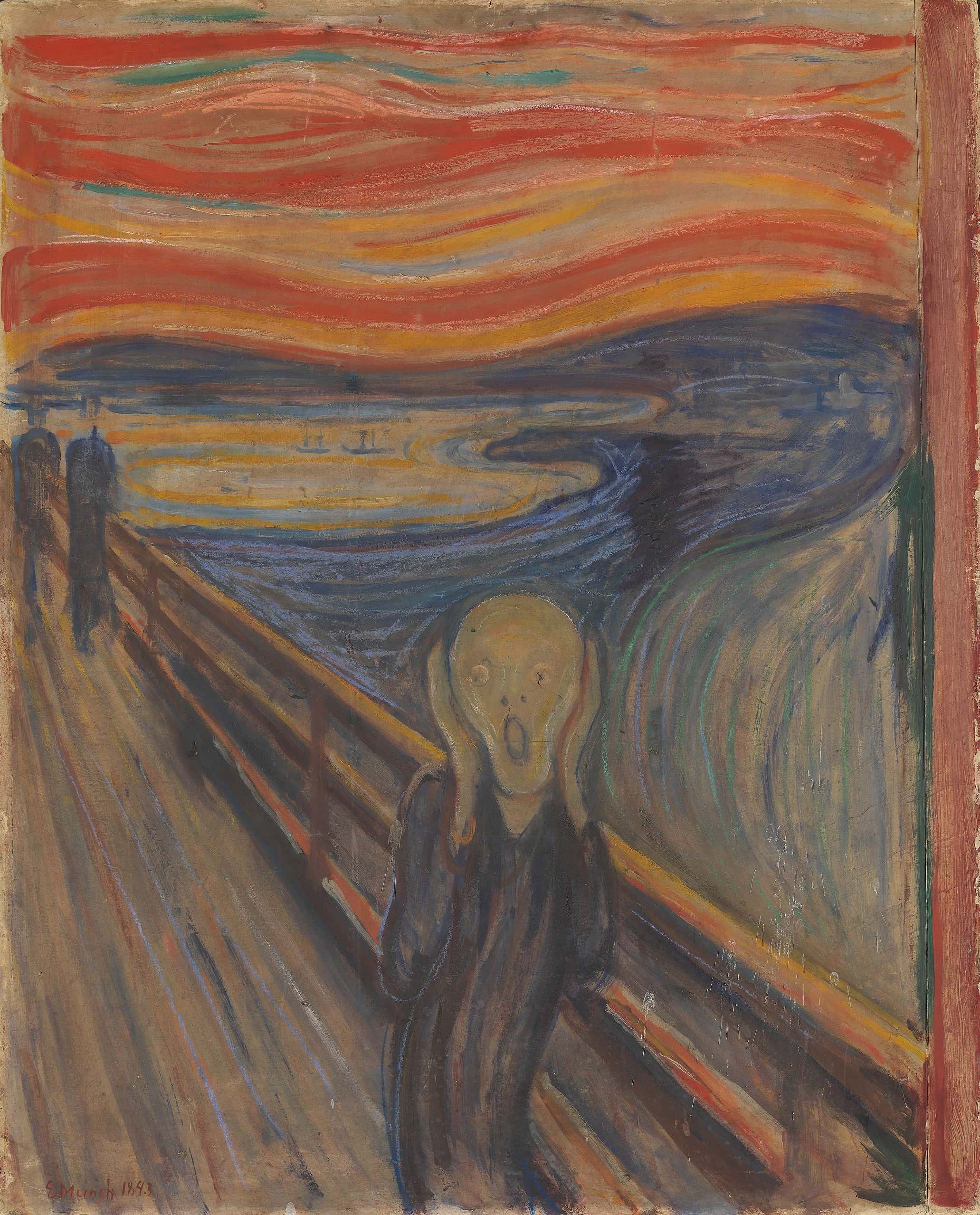

Edvard Munch: The Scream of Modern Anxiety
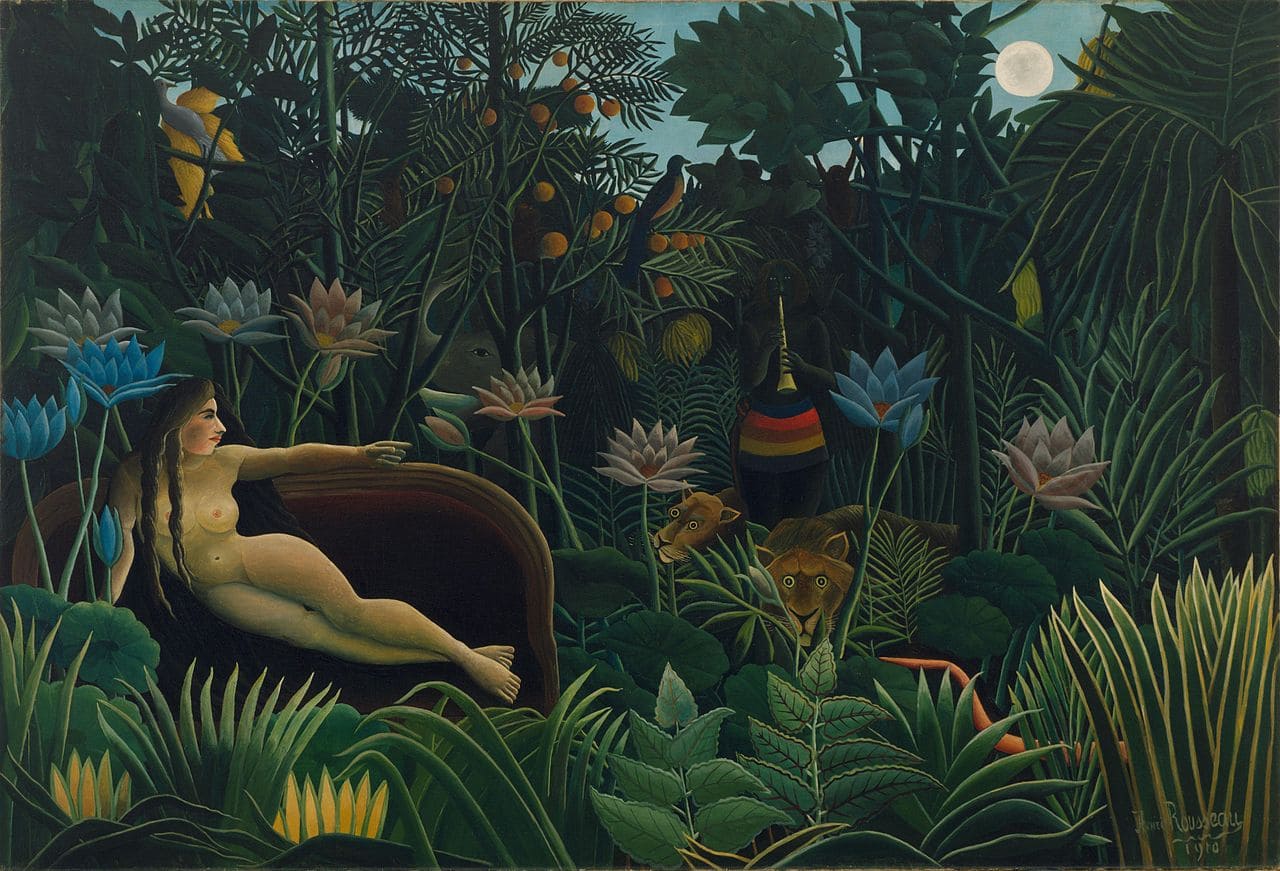

Henri Rousseau: The Naïve Dreamer

Camille Pissarro: The Impressionist-turned-Post-Impressionist
Lesson Details & Resources
In a Nutshell
- When: Late 19th to early 20th century
- Characteristics: Expressive color, symbolic content
- Key Artists: Vincent van Gogh, Paul Cézanne, Paul Gauguin
- Major Work: “Starry Night” by Vincent van Gogh
Vocabulary List
- Brushstroke
- The artist used bold and expressive brushstrokes to create movement in the painting.
- Palette
- The artist's palette consisted of vibrant colors that captured the essence of the post-impressionist style.
- Composition
- The composition of the painting was carefully planned to create a sense of balance and harmony.
- Impression
- The artist aimed to capture the fleeting impression of a moment in time.
- Texture
- The painting had a rich texture that added depth and dimension to the artwork.
- Contrast
- The artist used contrasting colors to create a dynamic and visually striking composition.
- Form
- The artist focused on capturing the form of the subject with precision and accuracy.
- Light
- Light played a crucial role in the artist's work, creating depth and atmosphere in the painting.
- Color theory
- The artist's understanding of color theory was evident in the vibrant and harmonious palette used in the artwork.
- Perspective
- The artist experimented with different perspectives to create a sense of depth and space in the painting.
- Symbolism
- The use of symbolic imagery added layers of meaning and complexity to the artwork.
- Abstraction
- The artist's work showed a move towards abstraction, breaking away from traditional representation.
- Balance
- The artist achieved a sense of balance in the composition through careful placement of elements.
- Gestural
- The gestural marks in the painting added a sense of energy and movement.
- Harmony
- The artist achieved a harmonious composition through the careful use of color and form.
- Expression
- The artist's work was full of emotion and expression, capturing the essence of the subject.
- Innovation
- The artist's innovative approach to painting pushed the boundaries of traditional art techniques.
- Vision
- The artist had a unique vision that set them apart from their contemporaries.
- Experimentation
- The artist's willingness to experiment with new techniques and styles led to groundbreaking artworks.
- Movement
- The painting captured a sense of movement and dynamism, drawing the viewer into the scene.
Timeline of Key Artists of Post-Impressionism: An Analysis
Paul Cézanne begins experimenting with geometric forms and structured compositions in his paintings, leading to the development of Cubism
Vincent van Gogh moves to Arles and creates some of his most famous works, including 'Starry Night'
Paul Gauguin travels to Tahiti and begins incorporating Polynesian themes and motifs into his paintings
Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec creates iconic posters for the Moulin Rouge cabaret in Paris
Georges Seurat develops the Pointillist technique, using small dots of color to create a cohesive image
Paul Signac joins Seurat in developing Pointillism and becomes known for his vibrant seascapes
Odilon Redon creates dreamlike and symbolic works using a combination of drawing and painting techniques
Edvard Munch paints 'The Scream', a haunting depiction of anxiety and despair
Pierre Bonnard and Edouard Vuillard form the Nabis group, focusing on decorative and symbolic art
Emile Bernard and Paul Sérusier develop the Synthetist style, emphasizing simplified forms and bold colors
Maurice Denis writes 'Definition of Neo-Traditionalism', outlining the principles of the Nabis group
Henri Rousseau begins painting his lush jungle scenes, inspired by visits to botanical gardens in Paris
Georges Rouault creates emotionally charged works with bold colors and thick brushstrokes
Aristide Maillol starts sculpting in a simplified, classical style influenced by ancient Greek art
Georges Braque begins working with Pablo Picasso, laying the groundwork for Cubism
Marc Chagall moves to Paris and starts incorporating Jewish themes and folklore into his paintings
Robert Delaunay experiments with color theory and abstraction in his 'Orphism' paintings
Fernand Léger develops a unique form of Cubism, emphasizing machine-like forms and geometric shapes
Kazimir Malevich paints 'Black Square', a seminal work in the development of abstract art
Giorgio de Chirico creates enigmatic, metaphysical paintings that influence Surrealism and Magical Realism
Key Facts
This is the information used in the fact matching game
- Post-Impressionism was a term coined by art critic Roger Fry in 1910 to describe the work of artists who were influenced by Impressionism but took their art in new directions.
- Key artists of Post-Impressionism include Vincent van Gogh, Paul Cézanne, Georges Seurat, and Paul Gauguin.
- Vincent van Gogh's use of vibrant colors and bold brushwork set him apart as one of the most iconic Post-Impressionist artists.
- Paul Cézanne's exploration of geometric forms and use of multiple perspectives had a significant influence on the development of Cubism.
- Georges Seurat is known for his technique of pointillism, in which small dots of color are applied to the canvas to create a sense of luminosity and harmony.
- Paul Gauguin's work often featured bold colors, simplified forms, and exotic subject matter inspired by his travels to Tahiti.
- Post-Impressionist artists were interested in exploring emotion, symbolism, and personal expression in their work.
- The use of bold, expressive brushwork was a common characteristic of Post-Impressionist painting.
- Post-Impressionism paved the way for the development of modern art movements such as Fauvism and Cubism.
- Post-Impressionist artists often rejected the idea of faithfully representing the natural world, instead focusing on capturing their own subjective experiences and emotions.
- Vincent van Gogh's painting 'Starry Night' is one of the most famous and recognizable works of Post-Impressionism.
- Paul Cézanne's 'Mont Sainte-Victoire' series of paintings explored the changing effects of light and color on the landscape.
- Georges Seurat's 'A Sunday Afternoon on the Island of La Grande Jatte' is a masterpiece of pointillism and is considered one of the most iconic works of Post-Impressionism.
- Paul Gauguin's 'Where Do We Come From? What Are We? Where Are We Going?' is a monumental painting that explores the themes of life, death, and the mysteries of existence.
- Post-Impressionist artists often experimented with new techniques and materials in their quest to express their inner visions and emotions.
- The legacy of Post-Impressionism can be seen in the work of later artists such as Henri Matisse, Pablo Picasso, and Wassily Kandinsky.
- Post-Impressionism was a diverse movement that encompassed a wide range of styles and approaches to art, reflecting the individuality and creativity of each artist.
- The term Post-Impressionism is a broad umbrella that encompasses a variety of artistic styles and movements that emerged in the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
- Post-Impressionist artists sought to push the boundaries of traditional painting and challenge the conventions of the art world.
- The innovative techniques and expressive qualities of Post-Impressionist art continue to inspire and influence artists and art lovers around the world.
Analysis & Significance
Historical Context
Post-Impressionism emerged in the late 19th century as a reaction against the limitations and constraints of Impressionism. Artists of this movement sought to further explore the use of color, form, and perspective in their works, often moving away from the strict adherence to naturalistic representation. This period was characterized by a time of rapid industrialization, urbanization, and social change, leading artists to experiment with new ways of expressing the world around them.
Defining Characteristics
Key visual and thematic elements of Post-Impressionism include vibrant colors, bold brushwork, and a focus on the emotional and psychological impact of the subject matter. Artists often distorted forms and perspectives to convey a sense of depth and movement in their works. Additionally, many Post-Impressionist artists were interested in exploring personal expression and subjective interpretations of reality, leading to a diverse range of styles and approaches within the movement.
Lasting Influence
Post-Impressionism had a significant influence on subsequent art movements, particularly the development of modern art in the 20th century. Artists such as Vincent van Gogh, Paul Cézanne, and Georges Seurat paved the way for new approaches to color, form, and composition that would later be explored by artists such as the Fauves, Cubists, and Expressionists. The legacy of Post-Impressionism can be seen in the continued emphasis on personal expression, experimentation with form, and the rejection of traditional academic conventions in art.
Key Artists of Post-Impressionism: An Analysis Games
Take Your Learning Offline
Want a convenient, print-ready study guide for this lesson? Become a Memory Wizards Pro member to unlock the downloadable " Memory Scrolls" for this topic and our entire library!
- ✓ Complete Vocabulary Lists
- ✓ Key Facts & Timelines
- ✓ Beautifully Formatted for Print & Mobile




