How Do You Learn Best?
Learn by Listening
Start with the 3-minute audio summary to get the key facts and narrative highlights quickly.
Learn by Reading
Immerse yourself in the 10-minute visual lesson for a comprehensive understanding of the topic.
Learn by Reviewing
Jump directly to the key facts, timeline, and vocabulary lists to build a solid foundation of details.
Learn by Doing
Challenge yourself! Jump straight into the interactive games to learn by trial, error, and discovery.
The Masterpiece: D'ou venons-nous?
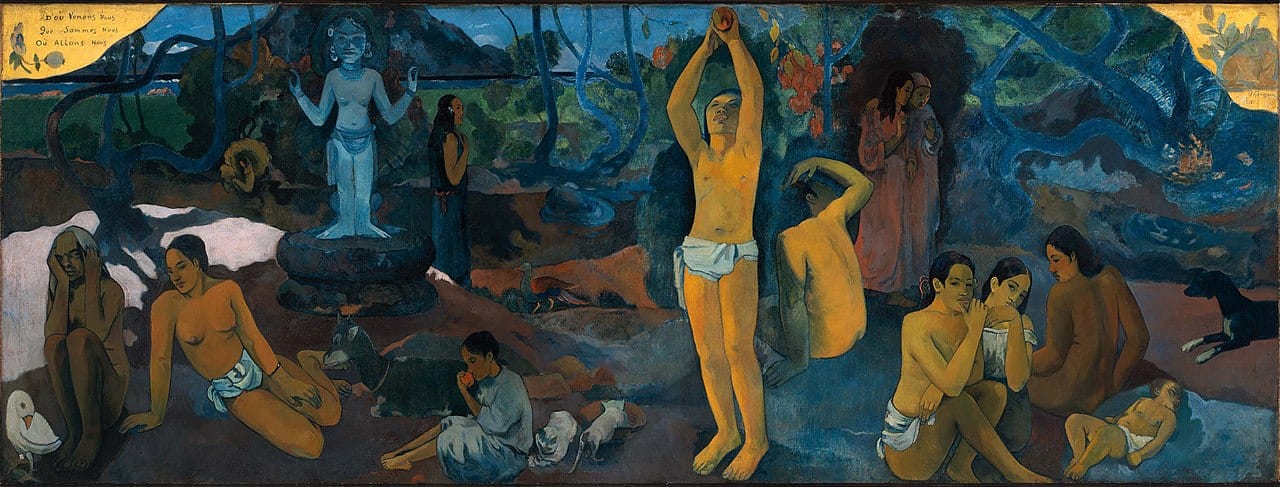

Deconstructing the Masterpiece
Tahitian Women
The depiction of native Tahitian women in traditional attire reflects Gauguin's interest in exoticism and primitivism.
Symbolic Still Life
Objects such as the idol, baby, and various fruits symbolize different stages of life and the cycle of birth and death.
Vibrant Color Palette
The bold and saturated colors used by Gauguin contribute to the overall dreamlike and otherworldly atmosphere of the painting.
Audio Library
As one of our featured lessons, this topic includes premium audio guides.
Paul Gauguin: An Analysis in 10 Minutes

The Early Years

Impressionist Connections

Exploration of Color

Symbolism in Art

Struggles and Successes

Personal Life

Influence on Modern Art

Late Career and Legacy
Rediscovery and Recognition
Lesson Details & Resources
In a Nutshell
- Paul Gauguin was born on June 7, 1848 in Paris, France.
- He was a French Post-Impressionist artist known for his colorful paintings.
- Gauguin was a successful businessman before turning to art in his mid-thirties.
- He was friends with fellow artist Vincent van Gogh and they influenced each other’s work.
- Gauguin is famous for his paintings of Tahiti, where he lived for several years.
- He died on May 8, 1903 in the Marquesas Islands at the age of 54.
Vocabulary List
- Tahiti
- Gauguin famously traveled to Tahiti to seek inspiration for his artwork.
- Primitivism
- Gauguin's work is often associated with the primitivist movement.
- Symbolism
- Many of Gauguin's paintings contain symbolic elements.
- Exotic
- Gauguin's use of vibrant colors and exotic subject matter set his work apart from his contemporaries.
- Mythical
- Gauguin often depicted mythical scenes in his paintings.
- Surreal
- Some of Gauguin's paintings have a surreal quality to them.
- Polynesia
- Gauguin's time in Polynesia greatly influenced his artistic style.
- Primitive
- Gauguin's art is characterized by its primitive, raw quality.
- Mystical
- There is a mystical quality to many of Gauguin's paintings.
- Nativity
- Gauguin painted a famous nativity scene during his time in Tahiti.
- Folklore
- Gauguin often drew inspiration from Polynesian folklore for his artwork.
- Colorful
- Gauguin's paintings are known for their bold and colorful palette.
- Goddess
- Gauguin frequently depicted Polynesian goddesses in his work.
- Dreamlike
- Many of Gauguin's paintings have a dreamlike quality to them.
- Mysterious
- There is a mysterious quality to Gauguin's art that continues to captivate viewers.
- Harmony
- Gauguin strived to create a sense of harmony in his compositions.
- Spiritual
- Gauguin's art often explores themes of spirituality and the divine.
- Jungle
- Gauguin painted lush jungle scenes during his time in Tahiti.
- Mythology
- Gauguin's work often references Polynesian mythology.
- Exoticism
- Gauguin's art is often characterized by its exoticism and otherworldly quality.
Timeline of Paul Gauguin: An Analysis
Paul Gauguin is born in Paris, France
Gauguin works as a stockbroker and begins painting in his free time
Gauguin marries Mette-Sophie Gad and moves to Copenhagen, Denmark
Gauguin's first son, Émile, is born
Gauguin returns to Paris and becomes friends with Camille Pissarro and other Impressionist artists
Gauguin travels to Martinique to paint tropical scenes
Gauguin moves to Arles, France to live and work with Vincent van Gogh
Gauguin moves to Tahiti in search of a more primitive and authentic culture
Gauguin's daughter, Aline, dies in childbirth
Gauguin completes his famous painting 'Where Do We Come From? What Are We? Where Are We Going?'
Gauguin travels to the Marquesas Islands and settles in the village of Atuona
Gauguin's health begins to deteriorate and he is diagnosed with syphilis
Gauguin dies in Atuona, Hiva Oa, Marquesas Islands
Gauguin's posthumous exhibition is held in Paris, showcasing his unique style and influence on modern art
Gauguin's works gain recognition and popularity in the art world
Gauguin's painting 'Nafea Faa Ipoipo' is sold for a record-breaking price at auction
Key Facts
This is the information used in the fact matching game
- Paul Gauguin was a French Post-Impressionist painter known for his bold use of color and simplified forms.
- Gauguin was a self-taught artist who began painting in his spare time while working as a stockbroker.
- He is best known for his paintings of Tahitian women and landscapes, which he created during his time living in Tahiti.
- Gauguin was a key figure in the Symbolist movement, which aimed to convey emotions and ideas through symbolic images.
- He often used flat, bright colors and simplified forms in his paintings, which influenced the development of modern art.
- Gauguin was a close friend of Vincent van Gogh, and the two artists shared a studio in Arles, France.
- In 1891, Gauguin traveled to Tahiti in search of a more primitive and exotic culture that he believed would inspire his art.
- During his time in Tahiti, Gauguin created some of his most famous works, including 'The Spirit of the Dead Watching' and 'Where Do We Come From? What Are We? Where Are We Going?'
- Gauguin's paintings often feature Tahitian women in traditional dress, surrounded by lush tropical landscapes.
- He was also a talented sculptor and woodcarver, creating intricate works inspired by Polynesian art.
- Gauguin's work was not widely appreciated during his lifetime, and he struggled financially for much of his career.
- Despite his struggles, Gauguin continued to experiment with new styles and techniques, pushing the boundaries of traditional art.
- After his death in 1903, Gauguin's work gained recognition and he became known as a pioneer of modern art.
- Today, Gauguin's paintings are considered some of the most important and influential works of the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
- Gauguin's use of color and form had a significant impact on the development of Fauvism and Expressionism.
- Several of Gauguin's paintings have sold for tens of millions of dollars at auction, making him one of the most valuable artists in history.
- In addition to his artistic pursuits, Gauguin was also a writer and a political activist, advocating for the rights of indigenous peoples in French colonies.
- Gauguin's work continues to inspire artists and art lovers around the world, with exhibitions of his paintings regularly held in major museums.
- Despite his controversial personal life and behavior, Gauguin's artistic legacy remains a significant part of art history.
- Gauguin's unique vision and innovative techniques have secured his place as one of the most important artists of the 19th century.
Analysis & Significance
Artistic Innovation
Paul Gauguin revolutionized the art world with his bold use of color, flattened perspectives, and simplified forms in his Post-Impressionist works. His departure from naturalistic representation towards more symbolic and emotive depictions paved the way for modern art movements like Fauvism and Expressionism.
Influence on Art History
Gauguin’s work inspired a generation of artists to explore new ways of expressing emotions and ideas through art. His rejection of traditional European painting techniques in favor of the exotic and primitive influenced artists like Pablo Picasso and Henri Matisse, leading to a shift in the definition of what art could be.
Cultural Significance Today
Today, Gauguin’s paintings are celebrated for their vivid colors, dreamlike compositions, and contemplative themes. His masterpiece, ‘Where Do We Come From? What Are We? Where Are We Going?’ continues to captivate audiences with its philosophical exploration of life and humanity, solidifying Gauguin’s legacy as a pioneering figure in the history of art.
Paul Gauguin: An Analysis Games
Take Your Learning Offline
Want a convenient, print-ready study guide for this lesson? Become a Memory Wizards Pro member to unlock the downloadable " Memory Scrolls" for this topic and our entire library!
- ✓ Complete Vocabulary Lists
- ✓ Key Facts & Timelines
- ✓ Beautifully Formatted for Print & Mobile




