At a Glance - Infographic
How Do You Learn Best?
Learn by Listening
Start with the 3-minute audio summary to get the key facts and narrative highlights quickly.
Learn by Reading
Immerse yourself in the 10-minute visual lesson for a comprehensive understanding of the topic.
Learn by Reviewing
Jump directly to the key facts, timeline, and vocabulary lists to build a solid foundation of details.
Learn by Doing
Challenge yourself! Jump straight into the interactive games to learn by trial, error, and discovery.
The Masterpiece: The Models- Georges Pierre Seurat
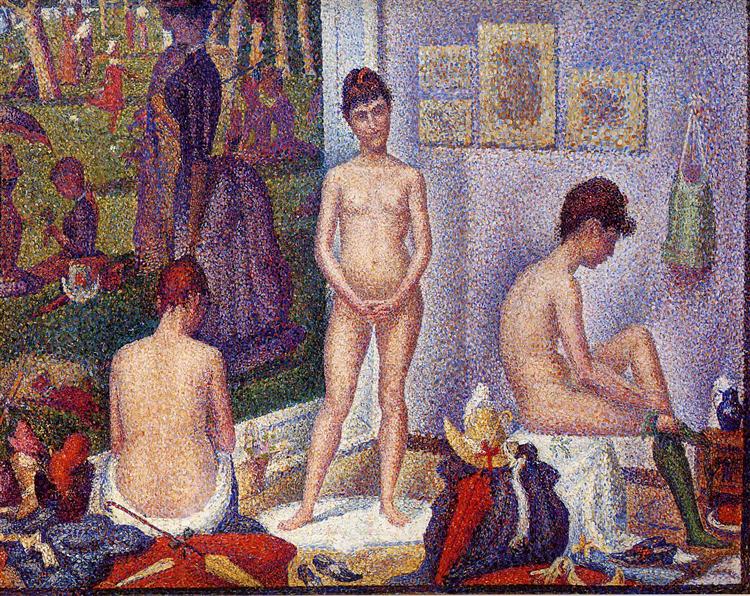
Deconstructing the Masterpiece
Pointillism Technique
Seurat's use of small dots of color, when viewed from a distance, creates a sense of luminosity and depth in the painting.
Composition
The careful arrangement of the models in the painting creates a balanced and harmonious composition, drawing the viewer's eye around the scene.
Natural Lighting
The soft, natural lighting in the painting adds a sense of realism and intimacy to the scene, highlighting the models' features.
Audio Library
As one of our featured lessons, this topic includes premium audio guides.
Georges Seurat: An Analysis in 10 Minutes

Early Life and Education
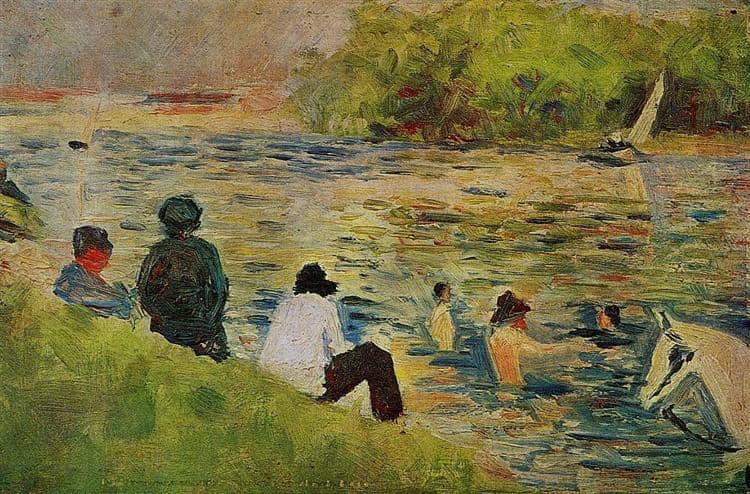
Development of Pointillism

Influence of Science
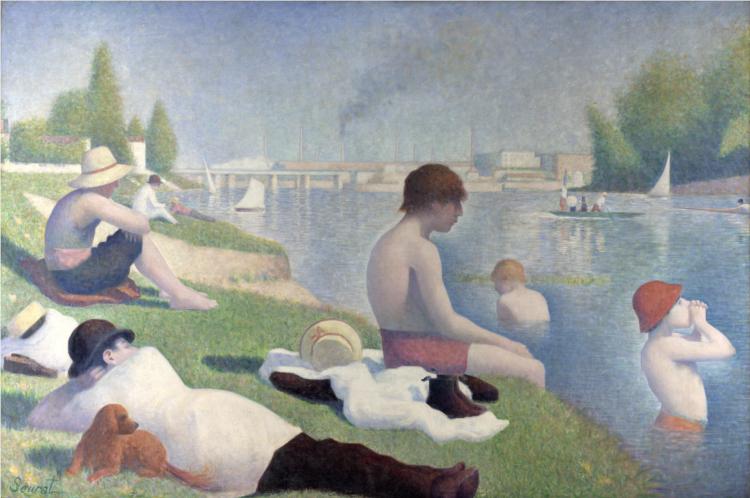

Neo-Impressionism Movement

Impact on Modern Art
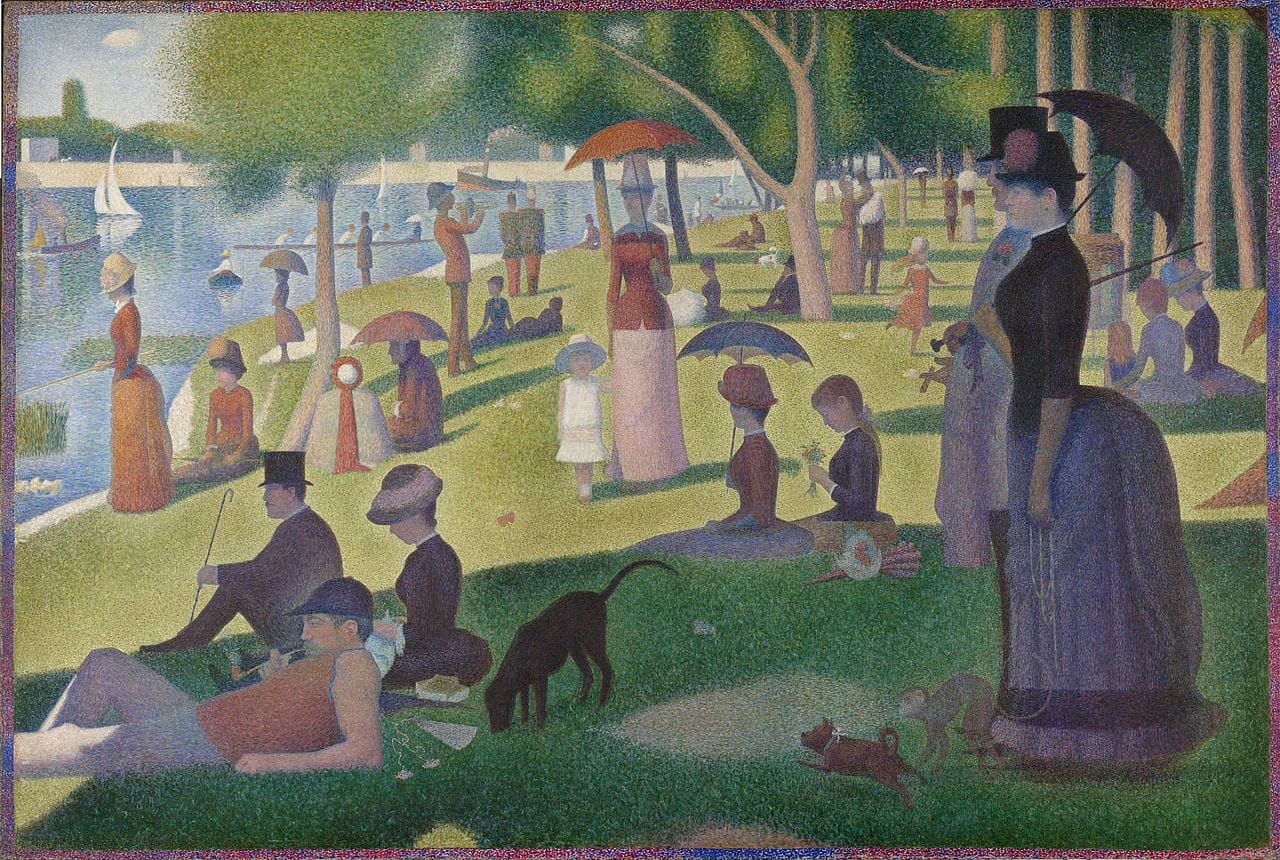
Legacy
Lesson Details & Resources
In a Nutshell
- Full Name: Georges Pierre Seurat
- Birthdate: December 2, 1859
- Birthplace: Paris, France
- Known For: Being a famous painter and the founder of Pointillism
- Education: Studied at the École des Beaux-Arts in Paris
- Most Famous Painting: “A Sunday Afternoon on the Island of La Grande Jatte”
- Style: Seurat was known for using tiny dots of color to create vibrant and detailed paintings
- Influence: His unique style of painting had a major impact on the development of modern art
Vocabulary List
- Pointillism
- Seurat was a pioneer of the pointillism technique, using small dots of color to create a cohesive image.
- Impressionism
- Seurat's work is often associated with impressionism, but he developed his own unique style within the movement.
- Chromoluminarism
- Seurat's use of color theory and light in his paintings is a key aspect of his chromoluminarism technique.
- Divisionism
- Divisionism is another term used to describe Seurat's pointillist technique, emphasizing the separation of colors.
- Optical mixing
- Seurat's use of small dots of color created an optical mixing effect, where colors blend together in the viewer's eye.
- Complementary colors
- Seurat often used complementary colors in his paintings to create contrast and harmony.
- Luminosity
- Seurat's paintings have a unique luminosity due to his use of pointillism and color theory.
- Brushstrokes
- Seurat's brushstrokes were meticulously planned and executed, reflecting his attention to detail.
- Form
- Seurat's paintings often focus on the form and structure of his subjects, creating a sense of solidity and volume.
- Light
- Light is a central theme in Seurat's work, with his use of color and composition to capture different qualities of light.
- Shadow
- Seurat's careful placement of shadows in his paintings adds depth and dimension to his compositions.
- Composition
- Seurat's compositions are carefully balanced and structured, with a focus on harmony and unity.
- Texture
- Seurat's use of pointillism creates a unique texture in his paintings, adding depth and complexity to the surface.
- Landscape
- Seurat painted many landscapes, using his pointillist technique to capture the natural beauty of the world around him.
- Urban
- Seurat also painted urban scenes, capturing the bustling energy of city life with his unique style.
- Figure
- Seurat's figures are often depicted with precise brushwork and attention to detail, creating a sense of realism.
- Modernism
- Seurat's work is often seen as a precursor to modernism, with its innovative use of color, light, and form.
- Harmony
- Harmony is a key element in Seurat's work, with his compositions carefully balanced to create a sense of unity.
- Contrast
- Seurat used contrast in his paintings to create visual interest and depth, playing light colors against dark.
- Balance
- Seurat's compositions are marked by a sense of balance and equilibrium, with every element carefully placed and considered.
Timeline of Georges Seurat: An Analysis
Georges Seurat is born in Paris, France
Seurat studies at the École des Beaux-Arts in Paris
Seurat begins to experiment with pointillism technique
Seurat's painting 'A Sunday Afternoon on the Island of La Grande Jatte' is exhibited at the Salon des Indépendants
Seurat's works are included in the final Impressionist exhibition in Paris
Seurat's painting 'Les Poseuses' is completed
Seurat's painting 'La Parade de Cirque' is completed
Seurat's painting 'Bathers at Asnières' is completed
Seurat's painting 'The Circus' is completed
Seurat co-founds the Société des Artistes Indépendants
Seurat's painting 'The Models' is completed
Seurat's painting 'The Channel of Gravelines, Petit Fort Philippe' is completed
Seurat's painting 'The Side Show' is completed
Seurat dies of an illness at the age of 31
Seurat's works continue to influence the development of modern art
Key Facts
This is the information used in the fact matching game
- Georges Seurat is known for developing the painting technique called Pointillism, which involved applying tiny dots of pure color to create a more vibrant image when viewed from a distance.
- Seurat's most famous work, 'A Sunday Afternoon on the Island of La Grande Jatte', took two years to complete and is considered a masterpiece of Pointillism.
- Seurat's use of color theory and optical mixing in his paintings had a significant influence on the development of modern art.
- Seurat was a founding member of the Neo-Impressionist movement, which sought to break away from the Impressionist style and explore new ways of depicting light and color.
- Seurat's early works were more traditional in style, but he gradually developed his Pointillist technique over time.
- Seurat's paintings often depict scenes of leisure and everyday life, such as picnics in the park or people strolling along the Seine river.
- Seurat's work was heavily influenced by the scientific theories of color and light of his time, particularly the work of chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul.
- Seurat's meticulous attention to detail and precise technique in his paintings earned him the nickname 'the engineer' among his peers.
- Seurat's use of Pointillism was a deliberate choice to create a more harmonious and balanced composition in his paintings.
- Seurat's work had a major impact on the development of Post-Impressionism and later movements such as Fauvism and Cubism.
- Seurat's painting 'La Parade' was one of the first works to showcase his fully developed Pointillist technique.
- Seurat's use of complementary colors in his paintings created a sense of harmony and balance in his compositions.
- Seurat's work was not widely appreciated during his lifetime, but he is now considered one of the most important artists of the 19th century.
- Seurat was influenced by Japanese prints and the work of Impressionist painters such as Claude Monet and Camille Pissarro.
- Seurat's painting 'Bathers at Asnières' showcases his early use of Pointillism and his interest in capturing light and shadow in outdoor scenes.
- Seurat's methodical approach to painting involved creating numerous preliminary sketches and studies before starting work on a final piece.
- Seurat's use of color in his paintings was influenced by the work of French chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul, who wrote about the optical mixing of colors.
- Seurat's painting 'The Circus' is another example of his Pointillist technique, with vibrant colors and intricate details.
- Seurat's work often depicted scenes of modern urban life in Paris, capturing the bustling energy and social interactions of the city.
- Seurat's innovative use of color and light in his paintings paved the way for later artists to explore new ways of representing the world around them.
Analysis & Significance
Artistic Innovation
Georges Seurat’s pointillist technique, using small dots of pure color to create a cohesive image, was a groundbreaking departure from traditional brushstrokes. This meticulous method allowed for a new level of optical blending and luminosity, giving his paintings a vibrant, almost pulsating quality that captivated viewers.
Influence on Art History
Seurat’s work laid the foundation for Neo-Impressionism, a movement that emphasized scientific color theory and the use of broken color to achieve greater harmony and depth. His innovative approach to painting influenced later artists such as Paul Signac and Henri Matisse, contributing to the development of modern art.
Cultural Significance Today
Today, Seurat’s masterpiece “A Sunday Afternoon on the Island of La Grande Jatte” continues to be celebrated as a monumental work of art. Its iconic status in art history and popular culture is a testament to Seurat’s enduring influence and the timeless appeal of his unique style. The painting’s meticulous detail and shimmering colors still captivate global audiences, making it a must-see for art enthusiasts around the world.
Georges Seurat: An Analysis Games
Take Your Learning Offline
Want a convenient, print-ready study guide for this lesson? Become a Memory Wizards Pro member to unlock the downloadable " Memory Scrolls" for this topic and our entire library!
- ✓ Complete Vocabulary Lists
- ✓ Key Facts & Timelines
- ✓ Beautifully Formatted for Print & Mobile




