At a Glance - Infographic
How Do You Learn Best?
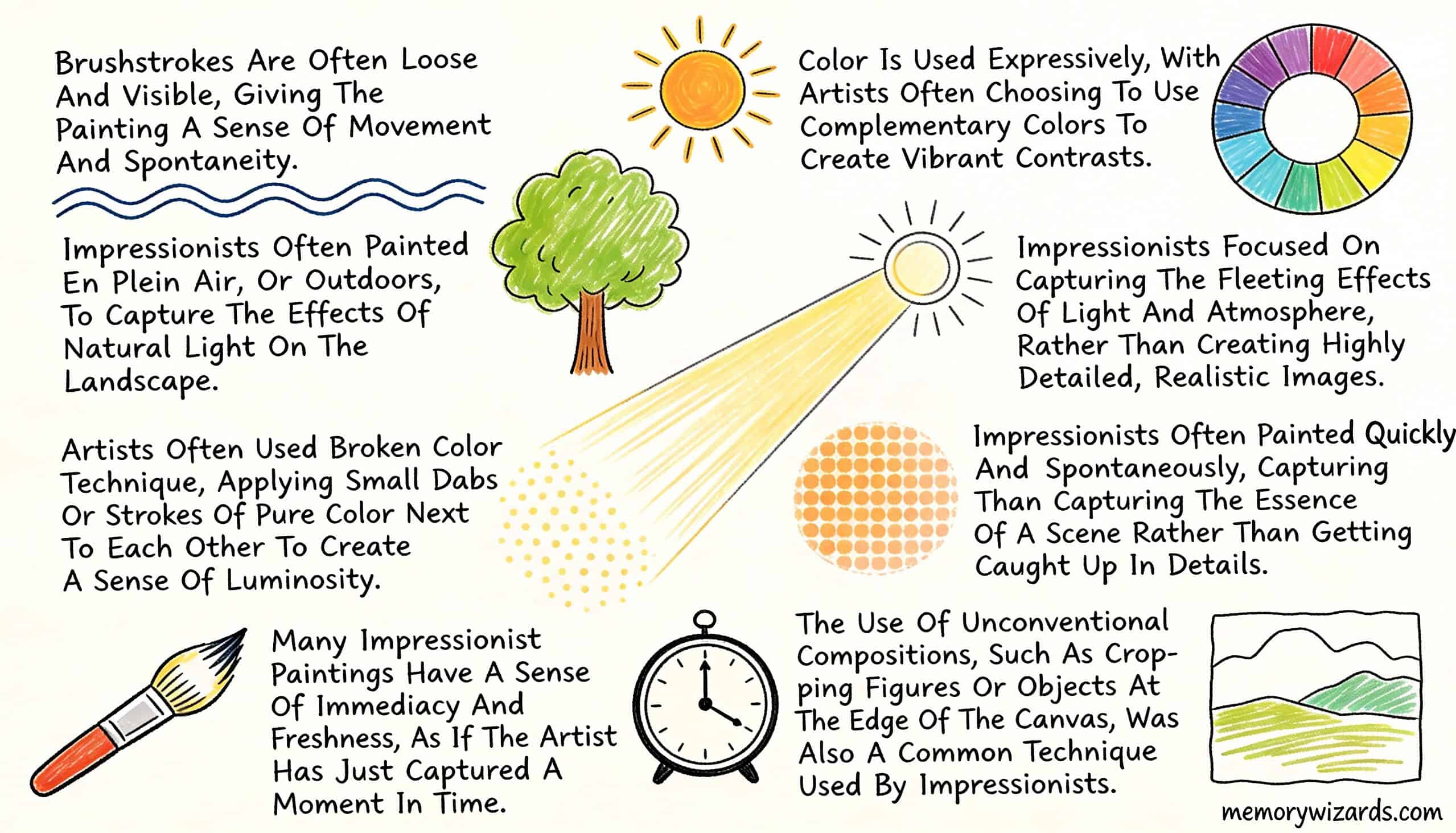
Learn by Listening
Start with the 3-minute audio summary to get the key facts and narrative highlights quickly.
Learn by Reading
Immerse yourself in the 10-minute visual lesson for a comprehensive understanding of the topic.
Learn by Reviewing
Jump directly to the key facts, timeline, and vocabulary lists to build a solid foundation of details.
Learn by Doing
Challenge yourself! Jump straight into the interactive games to learn by trial, error, and discovery.
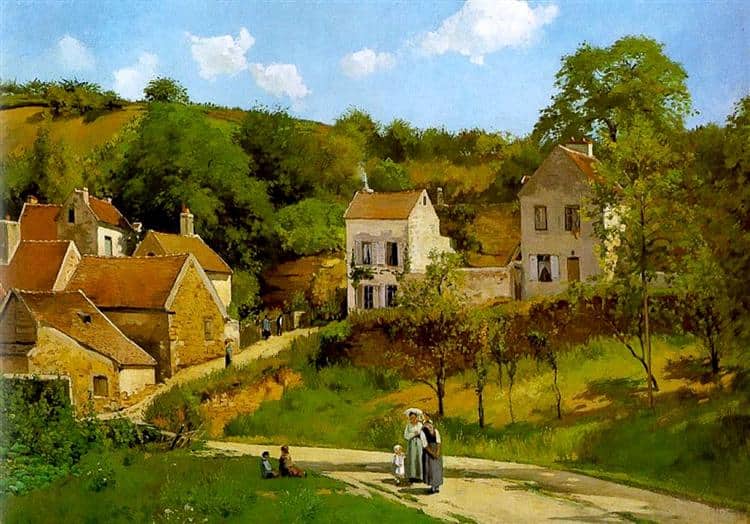
Example of Impressionist : Monet's Garden in Giverny

Deconstructing Impressionist
Broken Color
Using small, distinct brushstrokes of pure color to create a vibrant optical mixing effect and capture the changing qualities of light.
En Plein Air
Painting outdoors to capture natural light, atmosphere, and fleeting moments, emphasizing the artist's personal perception and immediate response to the scene.
Impressionistic brushwork
Loose, spontaneous brushwork that conveys movement, energy, and emotion, creating a sense of immediacy and capturing the essence of a subject rather than details.
Audio Library
As one of our featured lessons, this topic includes premium audio guides.
Unlock the Wizard's Cram Session
This powerful audio study guide is a Pro-exclusive feature. Upgrade to Memory Wizards Pro to access this and all of our premium learning tools.
Upgrade to ProImpressionist Techniques in 10 Minutes

1. Understanding Impressionism

2. Light and Color

3. Loose Brushwork

4. Capturing Movement
5. Composition and Framing

6. Texture and Surface

7. Atmospheric Effects

8. Reflections and Shadows

9. Subjectivity and Emotion

10. Legacy of Impressionism
Lesson Details & Resources
In a Nutshell
- When: The primary time period it flourished in.
- Characteristics: Its primary characteristics (2-3 keywords).
- Key Artists: 2-3 key artists associated with the movement.
- Major Work: A major work that exemplifies the style.
Vocabulary List
- Impasto
- The artist applied thick layers of paint to create a textured surface in the Impressionist painting.
- En plein air
- The artists often painted outdoors, capturing the effects of natural light and atmosphere.
- Luminosity
- Impressionist paintings often have a luminous quality due to the use of light and color.
- Brushwork
- Impressionist artists used loose and visible brushstrokes to create a sense of movement and spontaneity.
- Color theory
- Impressionists explored the science of color and its psychological effects on the viewer.
- Optical mixing
- Impressionist artists used small, distinct brushstrokes of pure color that the viewer's eye would blend together.
- Atmosphere
- Impressionists captured the changing qualities of light and atmosphere in their paintings.
- Broken color
- Impressionist artists used small touches of pure color to create the effect of shimmering light.
- Composition
- Impressionists often used unconventional compositions that focused on capturing a momentary impression.
- Subjectivity
- Impressionists aimed to convey their personal impressions and emotions through their artwork.
- Optical illusion
- Impressionist paintings often create the illusion of depth and movement through the use of color and light.
- Palette
- Impressionists used a wide range of colors on their palettes to capture the nuances of light.
- Reflection
- Impressionists often painted scenes that included reflections in water to explore the play of light and shadow.
- Soft focus
- Impressionists used soft edges and blurred outlines to create a dreamy and ethereal effect.
- Texture
- Impressionist paintings often have a tactile quality due to the varied application of paint.
- Tonalism
- Impressionists explored the use of light and shadow to create a sense of depth and atmosphere in their paintings.
- Urban scenes
- Impressionists depicted modern city life, capturing the hustle and bustle of urban environments.
- Visual perception
- Impressionists studied how the eye perceives color and light, leading to their innovative use of color.
- Watercolor
- Some Impressionist artists experimented with using watercolor techniques in their paintings.
- Whimsical
- Impressionist paintings often have a whimsical and dreamlike quality, evoking a sense of fantasy and imagination.
Timeline of Impressionist Techniques
Introduction of plein air painting techniques by Barbizon School artists
Exhibition of works by Edouard Manet and Claude Monet at the Salon des Refusés
Formation of the Société Anonyme Coopérative des Artistes Peintres, Sculpteurs, Graveurs
First independent exhibition of Impressionist artists
Critics use the term 'Impressionists' to describe the group of artists
Exhibition of Impressionist works at the first official Impressionist exhibition
Introduction of broken color technique by Impressionist artists
Development of the use of light and shadow in painting by Impressionists
Introduction of loose brushwork and visible brushstrokes by Impressionist artists
Influence of Japanese woodblock prints on Impressionist techniques
Introduction of the use of complementary colors by Impressionist artists
Exhibition of Impressionist works in New York City
Death of Claude Monet, one of the leading Impressionist artists
Recognition of the importance of Impressionism in the art world
Influence of Impressionist techniques on Post-Impressionist artists like Vincent van Gogh and Paul Cézanne
Influence of Impressionism on later art movements like Fauvism and Cubism
Exhibition of Impressionist works at major museums around the world
Continued study and appreciation of Impressionist techniques by art historians and critics
Legacy of Impressionism as a groundbreaking movement in the history of art
Key Facts
This is the information used in the fact matching game
- Impressionism was an art movement that originated in France in the 19th century.
- Impressionist artists often painted en plein air, or outdoors, to capture the effects of natural light.
- Impressionist artists used loose brushwork and visible brushstrokes to create a sense of movement and spontaneity in their paintings.
- Impressionist paintings often depict everyday scenes and subjects, such as landscapes, city streets, and people at leisure.
- Impressionist artists were influenced by scientific discoveries about color and light, such as the work of physicist Michel Eugène Chevreul.
- Impressionist artists sought to capture the fleeting effects of light and atmosphere in their paintings.
- Impressionist artists often painted quickly and spontaneously, in order to capture a momentary impression.
- Impressionist artists favored bright, vibrant colors and often used complementary colors to create a sense of harmony in their paintings.
- Impressionist paintings are known for their emphasis on light and shadow, and their use of broken color to create a sense of movement and depth.
- Impressionist artists were influenced by Japanese woodblock prints and the art of ukiyo-e, which emphasized flat patterns and bold compositions.
- Impressionist artists often painted the same scene at different times of day to capture the changing effects of light and atmosphere.
- Impressionist paintings are characterized by their emphasis on capturing a momentary impression, rather than creating a detailed, realistic image.
- Impressionist artists often left parts of their paintings unfinished, to suggest the fleeting nature of their subjects.
- Impressionist artists were interested in capturing the effects of modern life and technology in their paintings, such as trains, factories, and city streets.
- Impressionist artists often used thick impasto brushwork to create texture and depth in their paintings.
- Impressionist artists were influenced by the work of earlier artists such as Eugene Delacroix and Gustave Courbet, who also sought to capture the effects of light and atmosphere in their paintings.
- Impressionist artists were often criticized by traditional art critics for their loose brushwork and unconventional subject matter.
- Impressionism was a revolutionary movement in art that paved the way for later movements such as Post-Impressionism, Fauvism, and Cubism.
- Impressionist artists often exhibited their work independently of the official Salon exhibitions, in order to showcase their innovative techniques and subject matter.
- Impressionist paintings are now highly prized and sought after by collectors and museums around the world.
Analysis & Significance
Historical Context
The Impressionist movement emerged in France during the late 19th century, a time of great social and political change. This period saw the rise of the industrial revolution, urbanization, and the growing middle class. Artists were seeking new ways to capture the rapidly changing world around them, moving away from traditional academic styles towards more experimental and expressive techniques.
Defining Characteristics
Impressionist art is characterized by its emphasis on capturing the fleeting moment and the effects of light and color. Artists used loose brushwork and a vibrant color palette to convey the atmosphere and mood of a scene rather than focusing on precise details. They often painted outdoors, en plein air, to capture the changing light and atmosphere directly from nature.
Lasting Influence
The Impressionist movement had a profound impact on the art world, challenging traditional notions of art and paving the way for modern art movements such as Post-Impressionism, Fauvism, and Cubism. The emphasis on capturing the subjective experience of the artist and the use of color and light to convey emotion influenced generations of artists to come. Impressionism also had a lasting impact on popular culture, influencing fashion, design, and photography.
Impressionist Techniques Games
Take Your Learning Offline
Want a convenient, print-ready study guide for this lesson? Become a Memory Wizards Pro member to unlock the downloadable " Memory Scrolls" for this topic and our entire library!
- ✓ Complete Vocabulary Lists
- ✓ Key Facts & Timelines
- ✓ Beautifully Formatted for Print & Mobile




