At a Glance - Infographic

How Do You Learn Best?
Learn by Listening
Start with the 3-minute audio summary to get the key facts and narrative highlights quickly.
Learn by Reading
Immerse yourself in the 10-minute visual lesson for a comprehensive understanding of the topic.
Learn by Reviewing
Jump directly to the key facts, timeline, and vocabulary lists to build a solid foundation of details.
Learn by Doing
Challenge yourself! Jump straight into the interactive games to learn by trial, error, and discovery.
The Masterpiece: Edgar Degas: The Ballet Class

Deconstructing the Masterpiece
Naturalistic Setting
The realistic depiction of a rural landscape provides a sense of authenticity and connection to nature.
Human Interaction
The figures engaged in planting stakes suggest a narrative of labor and cooperation, adding a human element to the scene.
Horizontal Composition
The flat, horizontal arrangement of the elements creates a sense of stability and tranquility in the composition.
Audio Library
As one of our featured lessons, this topic includes premium audio guides.
Unlock the Wizard's Cram Session
This powerful audio study guide is a Pro-exclusive feature. Upgrade to Memory Wizards Pro to access this and all of our premium learning tools.
Upgrade to ProEdgar Degas: An Analysis in 10 Minutes

Introduction


Degas Discovers Impressionism

Exploring New Techniques

The Impressionist Movement

Degas Unique Style
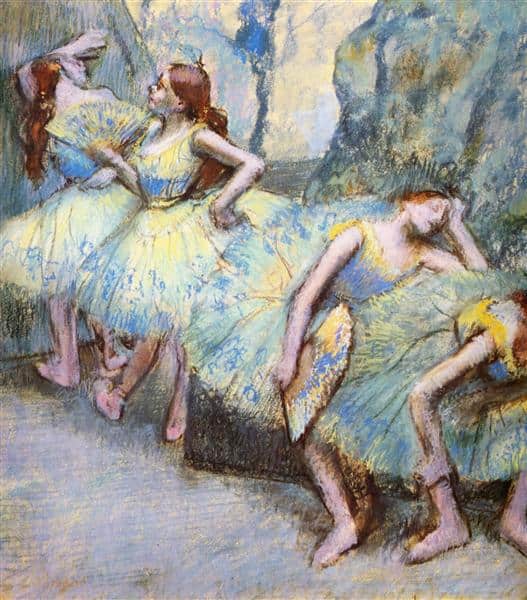
Subjects of Degas

Degas Legacy

Revisiting Degas Masterpieces


Lesson Details & Resources
In a Nutshell
- Artist: Edgar Degas
- Year: 1874
- Medium: Oil on canvas
- Location: Musée d’Orsay, Paris
Vocabulary List
- Impressionism
- Degas was a key figure in the Impressionist movement.
- Ballet
- Degas is famous for his paintings of ballet dancers.
- Pastel
- Degas often used pastels in his artwork.
- Ballerina
- Degas frequently depicted ballerinas in his paintings.
- Movement
- Degas was known for capturing movement in his artwork.
- Light
- Degas was a master at capturing the effects of light in his paintings.
- Composition
- Degas carefully considered the composition of his artwork.
- Sketch
- Degas created numerous sketches as studies for his paintings.
- Dancer
- Degas often painted dancers in various poses.
- Portrait
- Degas also created portraits of individuals.
- Studio
- Degas had a studio where he worked on his art.
- Brushstroke
- Degas used distinct brushstrokes in his paintings.
- Movement
- Degas captured the movement of dancers in his artwork.
- Elegant
- Degas' artwork often depicted elegant scenes.
- Texture
- Degas paid attention to the texture of objects in his paintings.
- Pose
- Degas' subjects often struck dramatic poses.
- Influence
- Degas' work had a significant influence on other artists.
- Exhibition
- Degas' work has been featured in many exhibitions.
- Inspiration
- Degas drew inspiration from everyday scenes and people.
- Technique
- Degas' painting technique was admired by his contemporaries.
Timeline of Edgar Degas: An Analysis
Edgar Degas is born in Paris, France
Degas begins studying at the École des Beaux-Arts in Paris
Travels to Italy and studies the works of Renaissance artists
Exhibits at the Salon for the first time
Becomes a founding member of the Impressionist group
Participates in the first Impressionist exhibition
Travels to New Orleans, Louisiana, USA to visit family members
Travels to visit family in Naples, Italy
Paints 'The Dance Class'
Participates in the fourth Impressionist exhibition
Paints 'The Absinthe Drinker'
Begins losing his eyesight
Paints 'The Tub'
Degas' eyesight deteriorates further, causing him to stop painting
Dies in Paris, France
Posthumous retrospective exhibition of Degas' work held at the Louvre
Degas' works continue to be exhibited and studied worldwide
Degas' art becomes highly regarded in the art world
Key Facts
This is the information used in the fact matching game
- Edgar Degas was a French artist famous for his paintings, sculptures, prints, and drawings.
- Degas is best known for his paintings of dancers, which capture movement and emotion with great skill.
- Degas was a leading figure in the Impressionist movement, although he preferred to be called a Realist or Independent.
- He was a master of capturing everyday scenes of Parisian life, such as cafes, theaters, and racecourses.
- Degas was known for his use of pastels, which he used to create vibrant and expressive works of art.
- He often painted his subjects from unusual angles, giving his works a sense of spontaneity and movement.
- Degas was a skilled draftsman and his drawings are highly prized for their precision and sensitivity.
- In addition to his paintings and drawings, Degas also created a number of sculptures, including his famous series of bronze dancers.
- Degas was influenced by Japanese prints and photography, which can be seen in his use of asymmetrical compositions and cropped figures.
- He was a perfectionist who often reworked his paintings and drawings multiple times before he was satisfied with the final result.
- Degas was a private person who rarely exhibited his work publicly and only sold a few of his paintings during his lifetime.
- Despite his reputation as a loner, Degas had a close circle of friends who were fellow artists, writers, and musicians.
- Degas suffered from failing eyesight in his later years, which affected his ability to create art, but he continued to work until his death.
- His works are now considered some of the most important and influential in the history of Western art.
- Degas' painting 'The Dance Class' is one of his most famous works and is a prime example of his skill in capturing movement and emotion.
- He was a master of light and shadow, using contrasting tones to create depth and drama in his compositions.
- Degas' style evolved over his career, moving from more traditional academic techniques to a looser, more expressive approach.
- He was fascinated by the human form and spent hours studying and sketching the figure in various poses and activities.
- Degas' work has had a lasting impact on modern art, influencing artists such as Pablo Picasso, Henri Matisse, and Mary Cassatt.
- Despite his contributions to the art world, Degas considered himself a failure and was often critical of his own work.
Analysis & Significance
Artistic Innovation
Edgar Degas revolutionized the art world with his innovative approach to capturing movement and light. His experimentation with composition, perspective, and unconventional angles brought a sense of dynamism and spontaneity to his works, particularly his ballet scenes and horse racing paintings.
Influence on Art History
Degas’ emphasis on movement and everyday life influenced the Impressionist movement and paved the way for modern art. His use of pastels and mixed media, as well as his focus on capturing fleeting moments and emotions, challenged traditional artistic norms and inspired future generations of artists.
Cultural Significance Today
Today, Degas’ work is celebrated for its timeless beauty and emotional depth. His depictions of dancers, racehorses, and Parisian life continue to captivate audiences around the world, showcasing the enduring power of his innovative techniques and unique perspective on the human experience.
Edgar Degas: An Analysis Games
Take Your Learning Offline
Want a convenient, print-ready study guide for this lesson? Become a Memory Wizards Pro member to unlock the downloadable " Memory Scrolls" for this topic and our entire library!
- ✓ Complete Vocabulary Lists
- ✓ Key Facts & Timelines
- ✓ Beautifully Formatted for Print & Mobile




