The Brain In A Vat (descartes' Evil Demon)
Is reality just an illusion created by a malevolent force?
How Do You Learn Best?
Learn by Reading
Immerse yourself in the 10-minute visual lesson for a comprehensive understanding of the topic.
Learn by Reviewing
Jump directly to the key facts, timeline, and vocabulary lists to build a solid foundation of details.
Learn by Doing
Challenge yourself! Jump straight into the interactive games to learn by trial, error, and discovery.
The Brain In A Vat in 10 Minutes
Introduction


Descartes
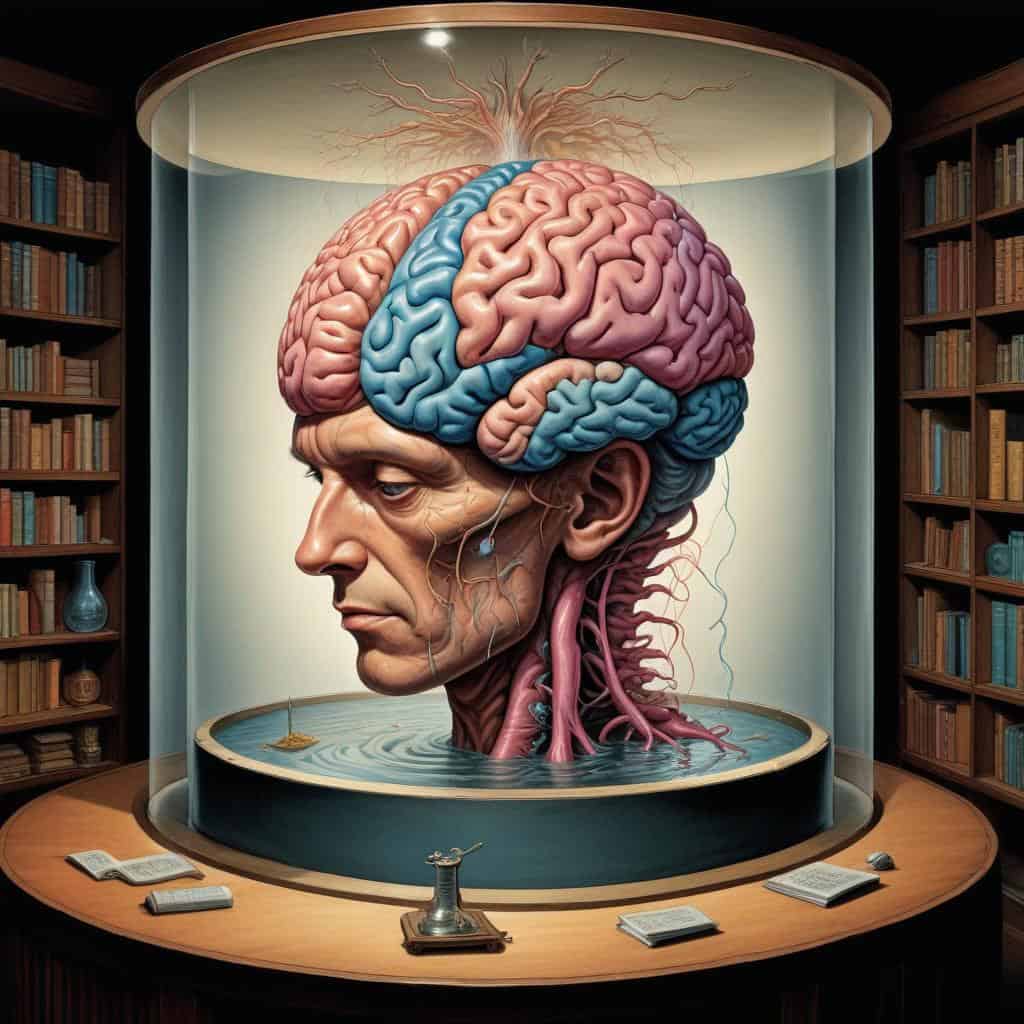

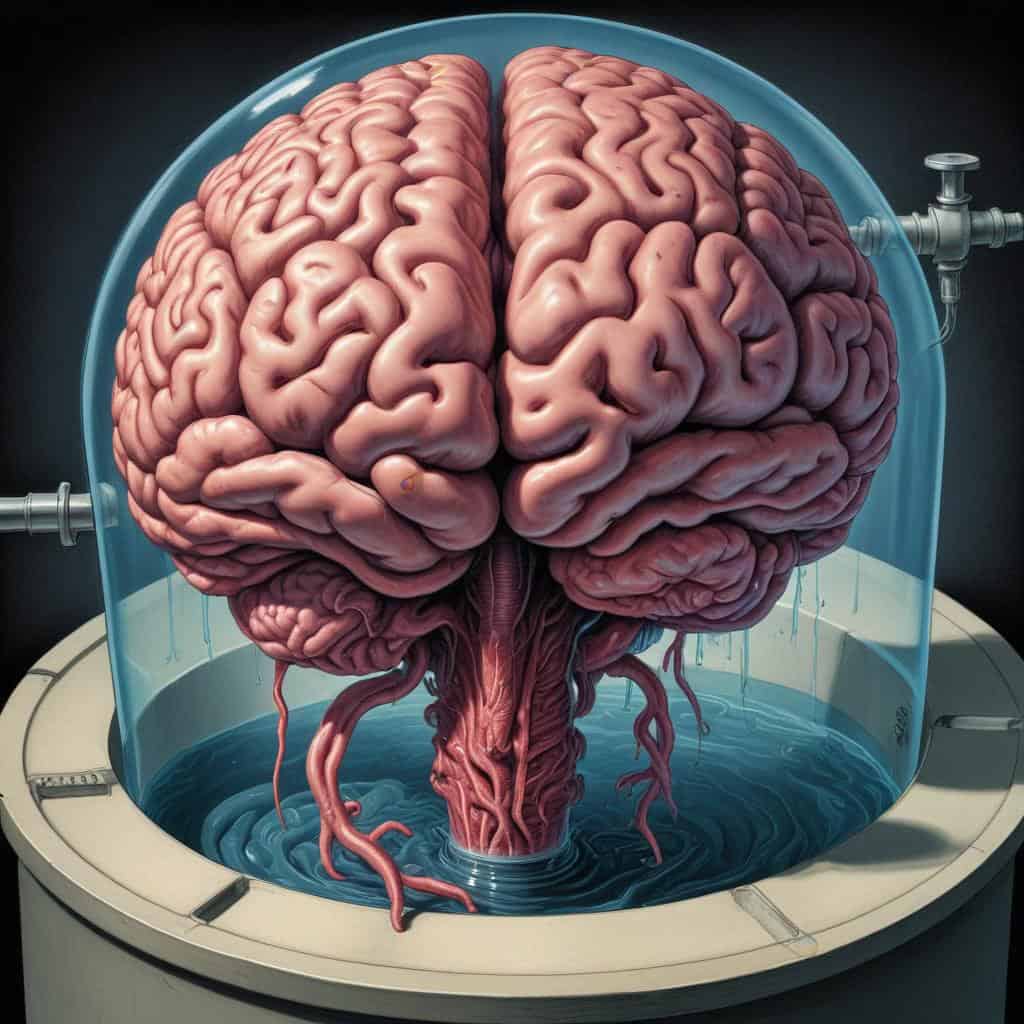
The Brain in a Vat

The Evil Demon
Simulated Reality

The Brain in a Vat (Descartes Evil Demon)

1. Introduction to the Scenario

2. Deception by the Evil Demon

3. Questioning the Nature of Reality

4. Doubt and Uncertainty

5. Philosophical Implications

6. Descartes Influence

7. Skepticism and Epistemology

8. Modern Interpretations

9. The Search for Truth
Lesson Details & Resources
In a Nutshell
- Concept: A thought experiment questioning the nature of reality and knowledge.
- Thinkers: René Descartes, 17th Century
- Central Question: Can we truly know if our perceptions of the world are real or if we are being deceived by an evil demon?
- Core Implication: The possibility that our reality may be an illusion, raising doubts about the certainty of our knowledge and understanding of the world.
Timeline of The Brain In A Vat
Descartes introduces the concept of the Evil Demon in 'Meditations on First Philosophy'
Descartes suggests that an evil demon could be deceiving him, casting doubt on all of his beliefs
Descartes raises the possibility that he is actually a brain in a vat being manipulated by the evil demon
The Brain in a Vat scenario becomes a popular topic of discussion among philosophers
Hilary Putnam introduces the modern version of the Brain in a Vat scenario in his paper 'Brains in a Vat'
The Brain in a Vat scenario is used to explore questions of reality, perception, and knowledge
Thought experiments involving the Brain in a Vat scenario are widely debated in philosophy circles
Philosophers like Daniel Dennett and Thomas Metzinger offer their own interpretations of the Brain in a Vat scenario
The Brain in a Vat scenario is featured in popular culture, including movies, TV shows, and books
Scientists and technologists explore the implications of the Brain in a Vat scenario for artificial intelligence and virtual reality
The ethical implications of the Brain in a Vat scenario are discussed in relation to issues like privacy and autonomy
Philosophers continue to use the Brain in a Vat scenario as a thought experiment to explore the nature of reality and consciousness
The Brain in a Vat scenario remains a controversial and thought-provoking concept in the field of philosophy
Vocabulary List
- Descartes' Evil Demon
- Descartes' Evil Demon is a concept used in philosophy to explore the limits of human knowledge and skepticism.
- Brain in a Vat
- The Brain in a Vat scenario raises questions about the nature of reality and the reliability of our senses.
- Skepticism
- Descartes' Evil Demon argument is often used as a way to illustrate the limits of human knowledge and the possibility of radical skepticism.
- Reality
- Descartes' Evil Demon challenges our understanding of reality and questions whether we can truly know the world as it is.
- Deception
- Descartes' Evil Demon raises concerns about the possibility of deception and the limitations of our ability to discern truth from falsehood.
Key Facts
This is the information used in the fact matching game
- Descartes' Evil Demon thought experiment posits the idea that an evil demon could be deceiving us into believing false perceptions of reality, including the existence of our own bodies and the external world.
- The Brain in a Vat scenario is a modern version of Descartes' Evil Demon, suggesting that our brains could be artificially stimulated to create false perceptions of reality while our bodies are actually in a vat of liquid.
- The Brain in a Vat scenario raises questions about the nature of reality, knowledge, and skepticism, as it challenges our beliefs about the external world and our own existence.
- If we cannot trust our sensory perceptions or reasoning abilities, then how can we be certain of anything we believe to be true? This is a central question raised by Descartes' Evil Demon and the Brain in a Vat scenario.
- Descartes used the Evil Demon thought experiment to demonstrate the possibility of radical skepticism, which calls into question the foundations of knowledge and the reliability of our cognitive faculties.
- The Brain in a Vat scenario also challenges our understanding of personal identity and the distinction between the mind and the body, as it suggests that our consciousness could exist independently of our physical bodies.
- Descartes' Evil Demon thought experiment has been influential in the development of modern epistemology and philosophy of mind, as it raises profound questions about the nature of reality and the limits of human understanding.
- The Brain in a Vat scenario has been explored in science fiction literature and films as a way to examine the implications of artificial intelligence, virtual reality, and the possibility of living in a simulated world.
- Some philosophers argue that even if we are brains in vats, the experiences and perceptions we have are still real in a certain sense, as they are the only reality we know and can interact with.
- Descartes' Evil Demon thought experiment serves as a powerful tool for challenging and refining our beliefs, as it forces us to critically examine the foundations of our knowledge and question the assumptions we often take for granted.
- The Brain in a Vat scenario highlights the limits of human perception and understanding, as it suggests that our experiences and beliefs could be manipulated by external forces beyond our control.
- The Brain in a Vat scenario has been used to explore ethical implications of artificial intelligence and the potential consequences of creating sentient beings with artificial consciousness.
- Descartes' Evil Demon thought experiment challenges the traditional notions of reality and truth, as it suggests that our perceptions and beliefs could be fundamentally mistaken or illusory.
- The Brain in a Vat scenario raises questions about the nature of free will and moral responsibility, as it challenges our assumptions about the autonomy of our choices and actions in a world where reality may be artificially constructed.
- Some philosophers argue that the Brain in a Vat scenario is not a useful thought experiment, as it leads to radical skepticism and undermines the possibility of knowledge and truth altogether.
- Descartes' Evil Demon thought experiment has been critiqued for its reliance on the concept of an omnipotent deceiver, as it raises questions about the nature of evil and the motivations of such a being to deceive us.
- The Brain in a Vat scenario challenges our assumptions about the nature of consciousness and the relationship between the mind and the external world, as it suggests that our perceptions could be entirely constructed by external forces.
- Descartes' Evil Demon thought experiment has been used to explore the nature of certainty and doubt, as it forces us to confront the possibility that our most fundamental beliefs and perceptions could be fundamentally mistaken.
- The Brain in a Vat scenario has implications for fields beyond philosophy, including neuroscience, psychology, and computer science, as it raises questions about the nature of consciousness, perception, and artificial intelligence.
- Descartes' Evil Demon thought experiment has been interpreted in various ways by philosophers, with some arguing that it demonstrates the limits of human knowledge and the necessity of skepticism, while others see it as a call to reaffirm our beliefs in the face of doubt and uncertainty.
Analysis & Significance
The Core Argument
The Brain in a Vat, also known as Descartes’ Evil Demon, posits that an individual’s sensory experiences and perceptions could be manipulated by an omnipotent deceiver to create a false reality. This challenges the certainty of one’s knowledge and raises questions about the nature of reality and existence.
Criticisms and Counterarguments
Critics argue that the Brain in a Vat scenario is merely a thought experiment with no practical implications for reality. They question the feasibility of such a scenario and the validity of doubting all perceptions. Some suggest that even if we are deceived, the very act of doubting implies a thinking entity.
Modern Relevance
The concept of the Brain in a Vat remains relevant in modern discussions surrounding artificial intelligence, virtual reality, and the ethics of technology. As advancements in technology blur the lines between reality and simulation, questions about the authenticity of experiences and the nature of consciousness become increasingly important. This philosophical idea challenges us to critically examine the role of perception and knowledge in an increasingly digital world.
The Brain In A Vat Games
Take Your Learning Offline
Want a convenient, print-ready study guide for this lesson? Become a Memory Wizards Pro member to unlock the downloadable " Memory Scrolls" for this topic and our entire library!
- ✓ Complete Vocabulary Lists
- ✓ Key Facts & Timelines
- ✓ Beautifully Formatted for Print & Mobile




