Summary of Treaty of Paris 1783
Unraveling the secrets of the Treaty of Paris 1783.
How Do You Learn Best?
Learn by Listening
Start with the 3-minute audio summary to get the key facts and narrative highlights quickly.
Learn by Reading
Immerse yourself in the 10-minute visual lesson for a comprehensive understanding of the topic.
Learn by Reviewing
Jump directly to the key facts, timeline, and vocabulary lists to build a solid foundation of details.
Learn by Doing
Challenge yourself! Jump straight into the interactive games to learn by trial, error, and discovery.
Audio Library
As one of our featured lessons, this topic includes premium audio guides.
Unlock the Wizard's Cram Session
This powerful audio study guide is a Pro-exclusive feature. Upgrade to Memory Wizards Pro to access this and all of our premium learning tools.
Upgrade to ProTreaty of Paris 1783 in 10 Minutes

Introduction

King George III

John Adams

Benjamin Franklin

John Jay

Charles James Fox

1. Negotiations Begin

2. Key Players

3. Terms of the Treaty

4. British Concessions

5. American Gains

6. Spanish Involvement

7. French Support

8. Ratification
9. Impact of the Treaty

10. Legacy

Lesson Details & Resources
In a Nutshell
- What: The Treaty of Paris 1783 marked the end of the American Revolutionary War.
- When: 1783
- Who: United States, Great Britain, France
- Outcome: The treaty recognized the independence of the United States and established the boundaries for the new nation.
Famous Figures in the Treaty of Paris 1783
-
Benjamin Franklin
Benjamin Franklin was one of the American negotiators who signed the Treaty of Paris 1783. He played a crucial role in securing favorable terms for the United States.
-
John Adams
John Adams, the second President of the United States, was another key negotiator of the Treaty of Paris 1783. He worked diligently to ensure American interests were protected.
-
John Jay
John Jay, an American statesman, was appointed as one of the peace commissioners to negotiate the Treaty of Paris 1783. He contributed to the successful conclusion of the treaty.
-
David Hartley
David Hartley was a British Member of Parliament who represented the British government in the negotiations for the Treaty of Paris 1783. He played a significant role in reaching an agreement.
-
Henry Laurens
Henry Laurens, an American merchant and diplomat, served as a peace commissioner for the United States during the negotiations for the Treaty of Paris 1783. He made valuable contributions to the process.
-
William Temple Franklin
William Temple Franklin, the grandson of Benjamin Franklin, acted as his grandfather's private secretary during the negotiations for the Treaty of Paris 1783. He assisted in documenting the proceedings.
Timeline of Treaty of Paris 1783
American Revolutionary War begins
Declaration of Independence
Battle of Yorktown
Preliminary Articles of Peace signed
Treaty negotiations begin in Paris
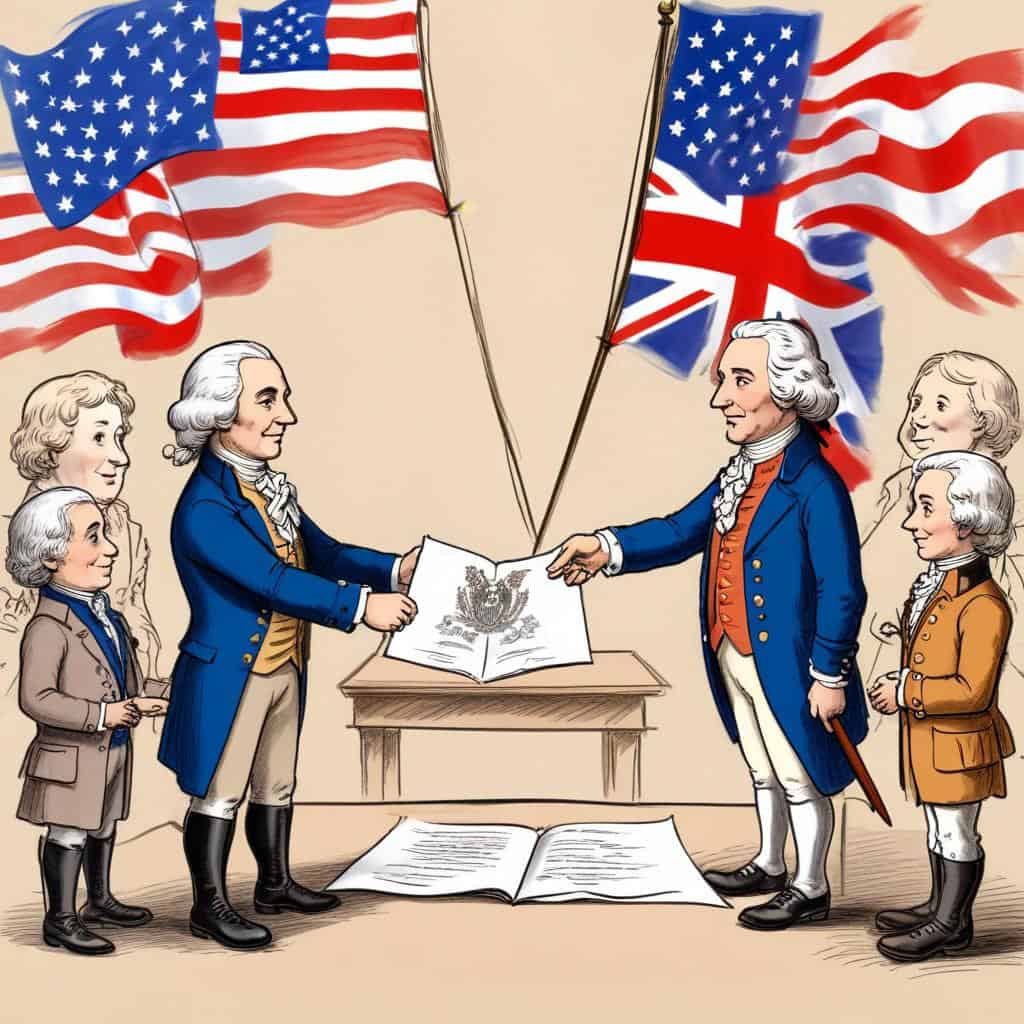
Treaty of Paris signed by United States
Treaty of Paris signed by Great Britain
British troops evacuate New York City
Last British troops leave Charleston
Continental Congress ratifies the Treaty of Paris
King George III formally ratifies the Treaty of Paris
American Revolutionary War officially ends
United States achieves formal independence
United States regains fishing rights off Newfoundland
United States receives all territory east of Mississippi River
United States agrees to restore loyalist property
United States agrees to recommend states restore confiscated loyalist property
United States agrees to prevent further confiscation of loyalist property
United States agrees to remove restrictions on British debts
United States agrees to allow creditors to collect pre-war debts
Vocabulary List
- Treaty
- The Treaty of Paris is a treaty that was signed in 1783.
- Paris
- The Treaty of Paris was signed in Paris, France.
- 1783
- The Treaty of Paris was signed in the year 1783.
- American Revolution
- The Treaty of Paris marked the end of the American Revolution.
- British
- The Treaty of Paris was signed between the United States and the British.
Key Facts
This is the information used in the fact matching game
- The Treaty of Paris 1783 officially ended the American Revolutionary War between Great Britain and the United States.
- The treaty was signed on September 3, 1783.
- It was negotiated in Paris, France.
- The treaty recognized the United States as an independent nation.
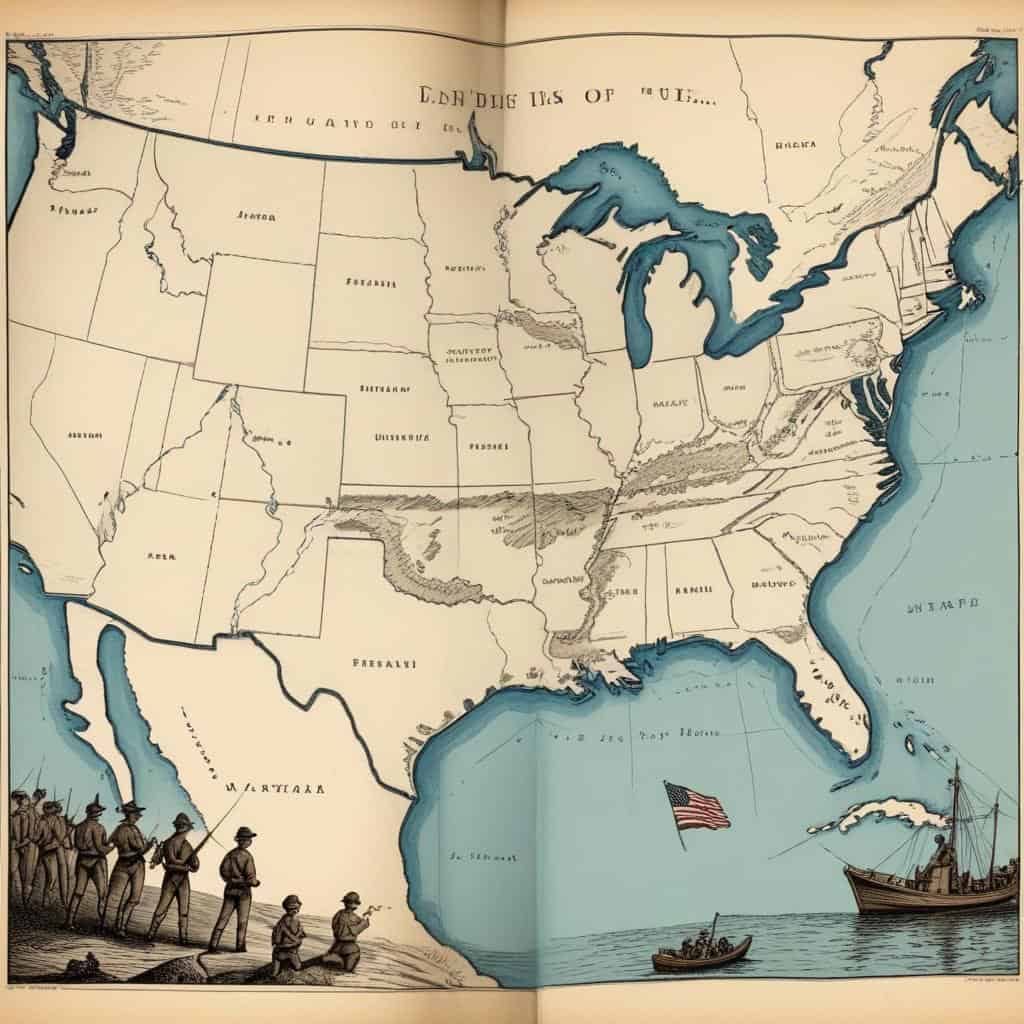
- Great Britain agreed to relinquish all claims to land south of the Great Lakes and east of the Mississippi River.
- The Mississippi River became the western boundary of the United States.
- The treaty established fishing rights for American fishermen off the coast of Newfoundland and in the Gulf of St. Lawrence.
- Great Britain agreed to withdraw all troops from American territory.
- The treaty included provisions for the return of American property confiscated during the war.
- The United States agreed to recommend that state legislatures restore property and rights to loyalists who had supported the British during the war.
- The treaty established a commission to resolve issues related to British debts owed by Americans and American debts owed to British creditors.
- The Treaty of Paris 1783 was instrumental in solidifying the United States as an independent nation.
- It marked the official recognition of the United States as a sovereign nation by Great Britain.
- The treaty was signed by John Adams, Benjamin Franklin, John Jay, and David Hartley.
- The Treaty of Paris 1783 set the stage for future diplomatic relations between the United States and Great Britain.
- It paved the way for further negotiations and treaties with other countries.
- The treaty established the boundaries of the United States, which would later expand through territorial acquisitions.
- The Treaty of Paris 1783 was ratified by the United States Congress on January 14, 1784.
- It marked the official end of the American Revolutionary War and the beginning of a new era for the United States.
- The Treaty of Paris 1783 remains one of the most significant treaties in American history.
Analysis & Significance
Immediate Consequences
Following the Treaty of Paris 1783, the American Revolutionary War officially came to an end, with Britain recognizing the United States as an independent nation. The treaty established the boundaries of the new nation and granted fishing rights to American fishermen off the coast of Canada.
Long-Term Impact
The Treaty of Paris 1783 marked a significant turning point in history, shaping the future of the United States and influencing global politics. It set the stage for the expansion of the United States westward and laid the foundation for the country’s development as a world power. The treaty also impacted the relationship between Britain and the United States, shaping diplomatic ties for generations to come.
Cultural Significance Today
The Treaty of Paris 1783 is remembered as a crucial moment in American history, symbolizing the country’s victory over British colonial rule and its emergence as a sovereign nation. The treaty’s legacy continues to influence international relations and serves as a reminder of the importance of diplomacy in resolving conflicts. It also highlights the enduring principles of freedom and self-determination that are cherished in American culture.
Treaty of Paris 1783 Games
Take Your Learning Offline
Want a convenient, print-ready study guide for this lesson? Become a Memory Wizards Pro member to unlock the downloadable " Memory Scrolls" for this topic and our entire library!
- ✓ Complete Vocabulary Lists
- ✓ Key Facts & Timelines
- ✓ Beautifully Formatted for Print & Mobile




