How Do You Learn Best?
Learn by Listening
Start with the 3-minute audio summary to get the key facts and narrative highlights quickly.
Learn by Reading
Immerse yourself in the 10-minute visual lesson for a comprehensive understanding of the topic.
Learn by Reviewing
Jump directly to the key facts, timeline, and vocabulary lists to build a solid foundation of details.
Learn by Doing
Challenge yourself! Jump straight into the interactive games to learn by trial, error, and discovery.
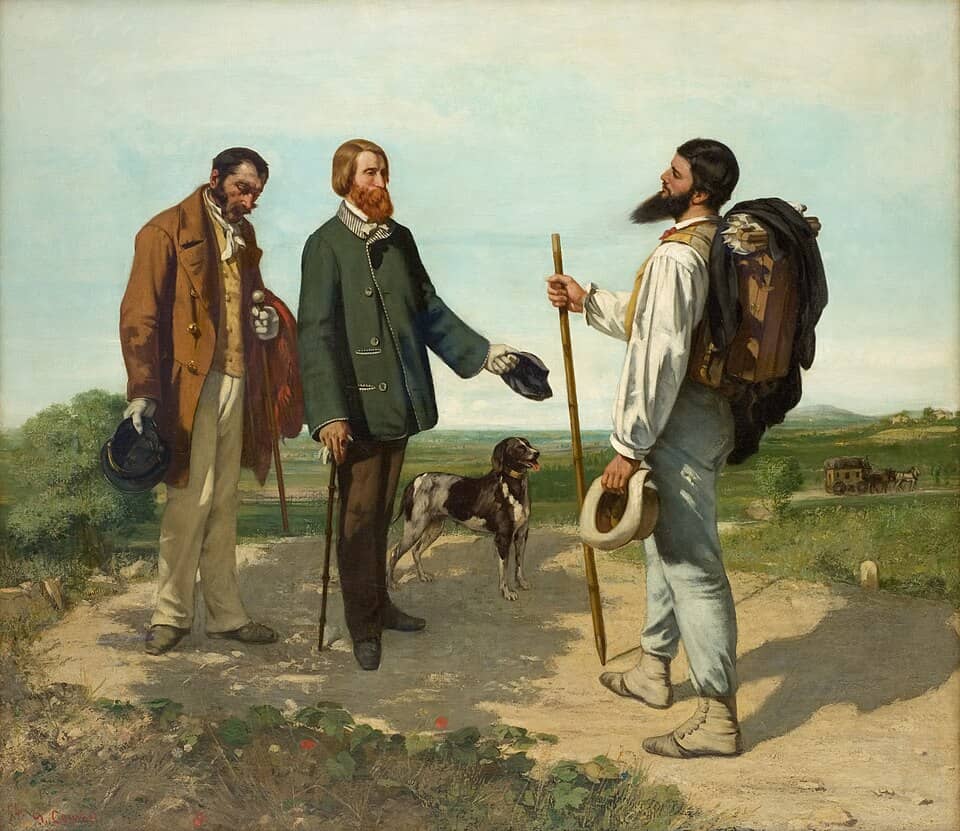
The Masterpiece: Courbet- The Meeting

Deconstructing the Masterpiece
No composition analysis points available.
Audio Library
As one of our featured lessons, this topic includes premium audio guides.
Unlock the Wizard's Cram Session
This powerful audio study guide is a Pro-exclusive feature. Upgrade to Memory Wizards Pro to access this and all of our premium learning tools.
Upgrade to ProIntroduction to Realism Art: An Analysis in 10 Minutes
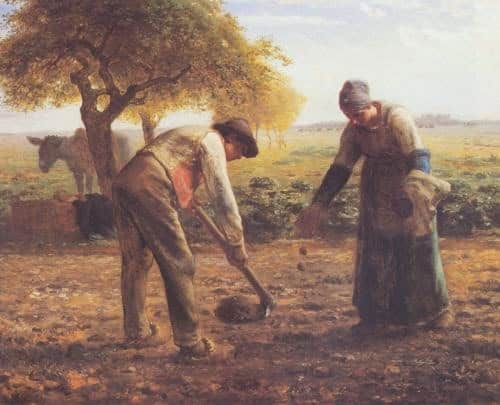

Introduction
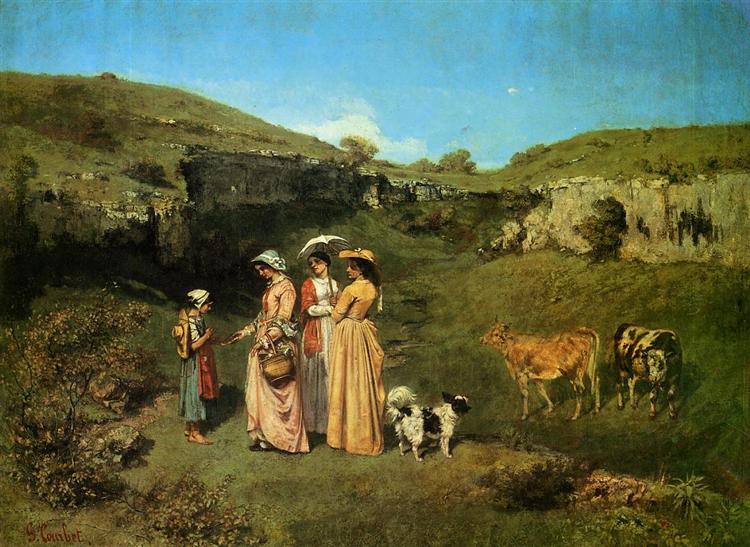
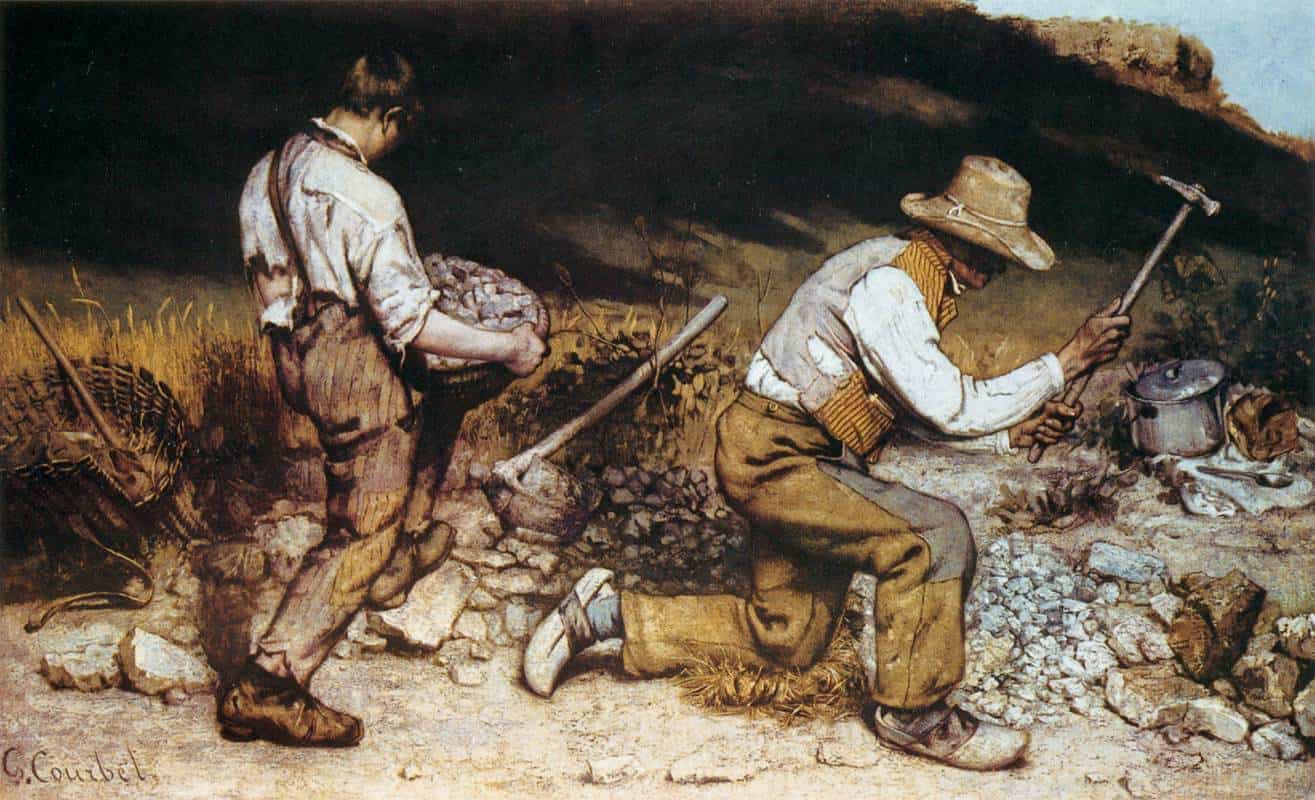
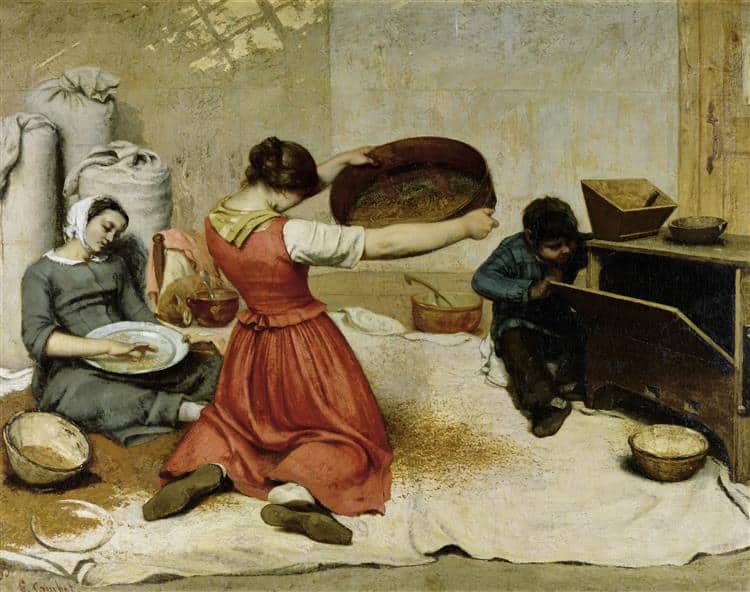



Gustave Courbet
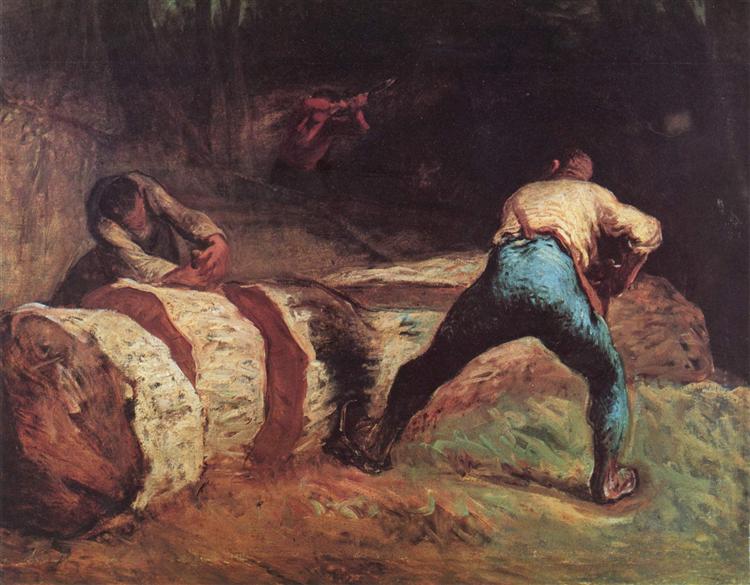

Jean-François Millet
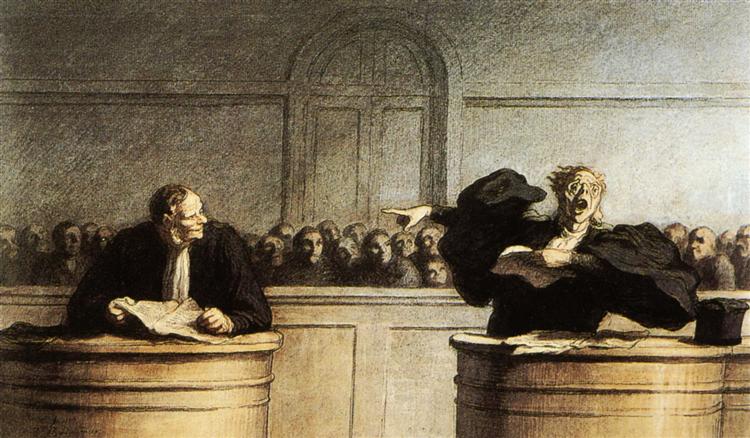

Honore Daumier

The Birth of Realism

Characteristics of Realism Art

Pioneers of Realism

Themes in Realism Art

Impact of Realism

Realism in Literature

Continuation of Realism

Appreciation for Realism Art

Realism in the Digital Age
Lesson Details & Resources
In a Nutshell
- Artist: Vincent van Gogh
- Year: 1889
- Medium: Oil on canvas
- Location: Museum of Modern Art, New York City
Vocabulary List
- Realism
- The artwork of 'Introduction to Realism Art by Realism' focuses on the concept of realism in art, which aims to depict subjects as they appear in real life.
- Artwork
- The exhibition 'Introduction to Realism Art by Realism' showcases various artworks created by realist artists, highlighting their techniques and themes.
- Subject
- In realist art, the subject refers to the main object or person depicted in the artwork, often portraying everyday scenes or individuals.
- Techniques
- Realist artists employ various techniques such as meticulous detailing, precise brushwork, and accurate proportions to create lifelike representations in their artwork.
- Lifelike
- Realism art strives to create lifelike representations that closely resemble the appearance of the subject in real life, often achieving a high level of realism.
- Detailing
- Realist artists pay great attention to detailing, capturing even the smallest elements or textures in their artwork to enhance the realism and depth.
- Proportions
- Maintaining accurate proportions is crucial in realist art to ensure that the size and scale of the subject accurately reflect its real-life counterpart.
- Palette
- Realist artists carefully select their color palette, often favoring natural tones and hues to recreate the realistic colors observed in the subject.
- Lighting
- Lighting plays a significant role in realist art, as artists use it to create shadows, highlights, and depth, contributing to the overall realism of the artwork.
- Still Life
- Realism art frequently includes still life compositions, representing inanimate objects such as fruits, flowers, or everyday items, often arranged in a carefully curated manner.
- Portraiture
- Realist artists excel in portraiture, capturing the likeness, expressions, and personality of individuals with meticulous attention to detail and realism.
- Landscapes
- Realism art often features landscapes, portraying natural scenery such as mountains, rivers, or fields with an emphasis on accurate representation and natural beauty.
- Urban Scenes
- Realist artists also depict urban scenes, capturing the hustle and bustle of city life with precision and authenticity, showcasing both architectural and human elements.
- Narrative
- Realism art can convey a narrative, telling a story or portraying a specific moment in time through the artwork's realistic depiction of the subject and its surroundings.
- Emotion
- Realist artists aim to evoke emotions in the viewers through their artwork, capturing the subtle nuances of human expressions and gestures with great sensitivity.
- Texture
- Realism art often incorporates texture, using various techniques to create the illusion of different textures, such as roughness, smoothness, or softness.
- Hyperrealism
- Hyperrealism is a genre within realism art that takes the concept of realism to an extreme level, often producing artworks that are almost indistinguishable from high-resolution photographs.
- Classic
- Realism art is often considered a classic style, drawing inspiration from the works of classical artists and placing importance on traditional artistic values.
- Contemporary
- While realism art has a rich history, it continues to be a relevant and contemporary style, with modern realist artists bringing new perspectives and subjects to the genre.
- Composition
- The composition in realist art refers to the arrangement and placement of elements within the artwork, ensuring a harmonious and balanced visual experience.
Timeline of Introduction to Realism Art: An Analysis
The term 'Realism' is first used to describe an artistic movement in France
Gustave Courbet's painting 'The Stone Breakers' is exhibited at the Paris Salon, sparking controversy for its depiction of ordinary laborers
Realism becomes a dominant artistic movement in Europe, focusing on depicting everyday life and social issues with accuracy and detail
Honore Daumier's lithographs critiquing French society are widely circulated, contributing to the popularity of Realism
The Realist movement spreads to other countries, including Germany, England, and the United States
Realist artists like Jean-Francois Millet and Thomas Eakins gain prominence for their depictions of rural life and urban scenes, respectively
Realism influences other art movements, such as Impressionism and Social Realism, leading to a diversification of artistic styles
Realism continues to be a significant force in art throughout the 20th century, with artists like Edward Hopper and Andrew Wyeth continuing the tradition
The principles of Realism, such as attention to detail and social commentary, remain relevant in contemporary art practice
Key Facts
This is the information used in the fact matching game
- Realism is an art movement that emerged in the mid-19th century in France.
- Realism sought to depict everyday life and the world as it is, without idealization or romanticism.
- Realist artists often focused on ordinary people and their daily activities.
- Realism was a response to the idealized and romanticized art of the time, such as Romanticism.
- Realist paintings often feature detailed and accurate depictions of scenes and subjects.
- Realism was influenced by social and political changes, such as the Industrial Revolution and the rise of photography.
- Realist artists often used techniques such as chiaroscuro and perspective to create realistic effects.
- Realist art often explores themes such as poverty, labor, and social inequality.
- Realist artists were interested in depicting the effects of industrialization and urbanization on society.
- Realism paved the way for later art movements, such as Impressionism and Social Realism.
- Realist artists often painted en plein air, or outdoors, to capture natural light and atmosphere.
- Realism was influenced by the writings of authors such as Gustave Flaubert and Emile Zola.
- Realist art often features a sense of immediacy and authenticity, as if the viewer is witnessing a moment in time.
- Realism challenged traditional artistic conventions and sought to represent the world in a new and truthful way.
- Realist artists often depicted the struggles of working-class people and the harsh realities of urban life.
- Realism was influenced by the rise of positivism and scientific thinking in the 19th century.
- Realist art often features muted colors and a focus on capturing the textures and details of everyday objects.
- Realism was criticized by some for its perceived lack of idealism and beauty, but praised for its honesty and social commentary.
- Realist artists often painted from life and made sketches and studies before creating their final works.
- Realism continues to influence contemporary artists and is seen as a powerful and relevant artistic movement.
Analysis & Significance
Artistic Innovation
Introduction to Realism Art marked a departure from the idealized and romanticized portrayals of the past, focusing instead on capturing ordinary scenes and people with meticulous detail and accuracy. Artists such as Gustave Courbet and Jean-François Millet emphasized the beauty in everyday life, challenging traditional conventions and giving a voice to the common man.
Influence on Art History
This movement laid the foundation for modern art by prioritizing truthfulness and authenticity in representation. Realism Art inspired later artists to explore social issues, depict the harsh realities of industrialization, and champion the working class. It also paved the way for other movements like Impressionism and Surrealism, shaping the course of art history.
Cultural Significance Today
Realism Art continues to resonate with contemporary audiences for its raw honesty and emotional impact. The artworks from this period serve as historical records, shedding light on the societal challenges and struggles of the time. Their enduring relevance reminds us of the power of art to reflect and critique the world around us, making them timeless masterpieces that continue to inspire and provoke thought.
Introduction to Realism Art: An Analysis Games
Take Your Learning Offline
Want a convenient, print-ready study guide for this lesson? Become a Memory Wizards Pro member to unlock the downloadable " Memory Scrolls" for this topic and our entire library!
- ✓ Complete Vocabulary Lists
- ✓ Key Facts & Timelines
- ✓ Beautifully Formatted for Print & Mobile




