How Do You Learn Best?
Learn by Reading
Immerse yourself in the 10-minute visual lesson for a comprehensive understanding of the topic.
Learn by Reviewing
Jump directly to the key facts, timeline, and vocabulary lists to build a solid foundation of details.
Learn by Doing
Challenge yourself! Jump straight into the interactive games to learn by trial, error, and discovery.
The Masterpiece: Son-Of-Man

Deconstructing the Masterpiece
Apple
The apple covering the man's face creates a sense of mystery and obscurity, inviting viewers to question the identity of the figure.
Bowler Hat
The bowler hat symbolizes conformity and anonymity, contrasting with the surreal juxtaposition of the floating apple.
Green Apple
The bright green apple stands out against the dark background, drawing attention to the significance of the obscured face.
Faceless Figure
The faceless figure challenges traditional portraiture by concealing the subject's identity, prompting viewers to contemplate the nature of perception and reality.
René Magritte: An Analysis in 10 Minutes

Introduction
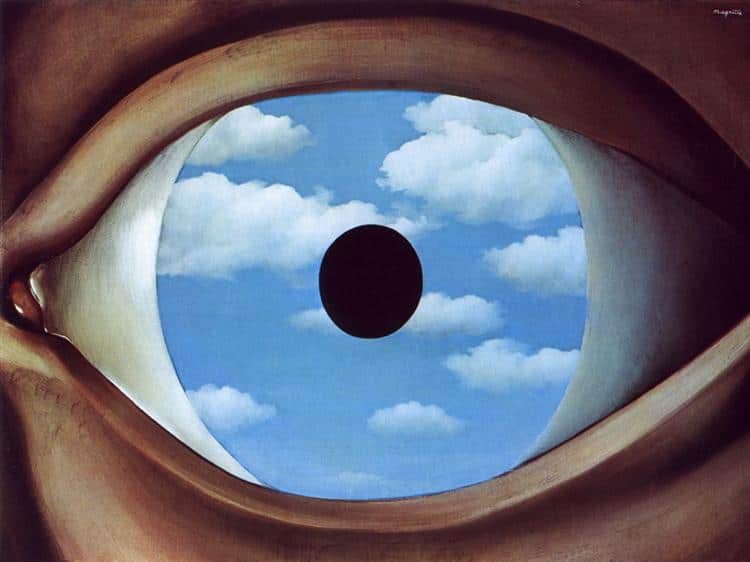



The Early Years of René Magritte

Magrittes Breakthrough in Surrealism
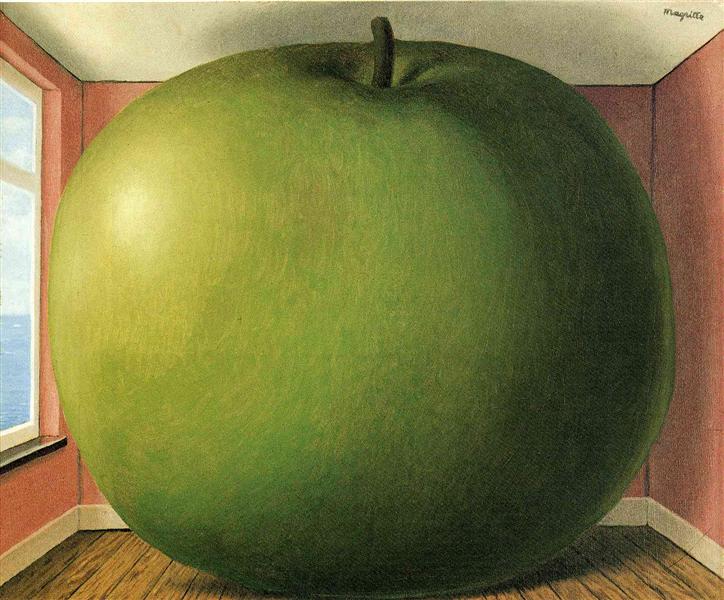

The Key Themes in Magrittes Work
Magrittes Influence on Surrealism

The Later Years of René Magritte
Lesson Details & Resources
In a Nutshell
- Artist: René Magritte
- Year: 1928
- Medium: Oil on canvas
- Location: Los Angeles County Museum of Art, Los Angeles
Vocabulary List
- Surrealism
- Magritte was a prominent figure in the surrealist movement, known for his dream-like imagery and exploration of the subconscious.
- Illusion
- Magritte often played with the concept of illusion in his artwork, creating scenes that challenge the viewer's perception of reality.
- Mystery
- Magritte's paintings are full of mystery and ambiguity, inviting viewers to question what they see.
- Enigma
- Magritte's work is often described as enigmatic, with layers of meaning that are open to interpretation.
- Symbolism
- Magritte used symbols and visual metaphors in his artwork to convey deeper meanings.
- Juxtaposition
- Magritte frequently juxtaposed ordinary objects in his paintings to create unexpected and thought-provoking compositions.
- Metamorphosis
- Magritte's work often features objects undergoing metamorphosis or transformation, blurring the boundaries between reality and fantasy.
- Absurdity
- Magritte's paintings often contain elements of absurdity, challenging conventional logic and inviting viewers to question the nature of reality.
- Identity
- Magritte's artwork often explores themes of identity and the self, questioning how we define ourselves in relation to the world around us.
- Perception
- Magritte's work challenges the viewer's perception of reality, inviting them to question what they see and how they interpret it.
- Displacement
- Magritte frequently depicted objects in unexpected or illogical positions, creating a sense of displacement and unease in his paintings.
- Paradox
- Magritte's work often contains paradoxical elements, such as impossible objects or contradictory imagery.
- Reflection
- Magritte's paintings often feature mirrors and reflections, inviting viewers to contemplate ideas of duality and self-reflection.
- Repetition
- Magritte's work sometimes incorporates repetitive motifs or images, creating a sense of rhythm and pattern in his paintings.
- Ambiguity
- Magritte's paintings are characterized by ambiguity and open-ended interpretations, allowing viewers to bring their own meanings to his work.
- Subversion
- Magritte's artwork often subverts traditional notions of reality and representation, challenging viewers to think differently about the world around them.
- Mystification
- Magritte's work is known for its mystifying qualities, drawing viewers into a world of uncertainty and wonder.
- Duality
- Magritte frequently explored themes of duality and opposites in his artwork, questioning the nature of opposition and contradiction.
- Deception
- Magritte's paintings often contain elements of deception and trickery, inviting viewers to question what is real and what is an illusion.
- Disruption
- Magritte's work disrupts traditional modes of representation, challenging viewers to reconsider their assumptions about art and reality.
Timeline of René Magritte: An Analysis
René Magritte is born in Lessines, Belgium
Magritte's mother drowns herself in the River Sambre
Magritte attends the Académie Royale des Beaux-Arts in Brussels
Magritte meets Georgette Berger, who becomes his wife and muse
Magritte joins the Belgian Surrealist group
Magritte's first solo exhibition in Brussels
Magritte creates 'The Treachery of Images' (Ceci n'est pas une pipe)
Magritte moves to Paris and becomes friends with André Breton and Salvador Dalí
Magritte returns to Brussels due to the outbreak of World War II
Magritte's work gains international recognition
Magritte's mother's body is exhumed and identified, impacting his art
Magritte dies of pancreatic cancer in Brussels
Magritte's work continues to influence artists and thinkers worldwide
Key Facts
This is the information used in the fact matching game
- René Magritte was a Belgian surrealist artist known for his thought-provoking paintings that challenged the viewer's perception of reality.
- Magritte's work often featured ordinary objects in unusual contexts, creating a sense of mystery and intrigue.
- One of Magritte's most famous paintings is 'The Son of Man', which features a man in a bowler hat with an apple obscuring his face.
- Magritte's art is characterized by clean, precise lines and a deadpan style that belies the deeper meaning behind his images.
- Magritte often used wordplay and puns in his artwork, challenging viewers to think about the relationship between images and words.
- Magritte's work has influenced many artists and writers, including the pop art movement and the French philosopher Michel Foucault.
- Magritte's paintings often feature a sense of dislocation or unreality, as if the objects depicted are out of place or don't belong.
- Magritte's use of everyday objects like pipes and apples in his artwork challenges traditional ideas of representation and symbolism.
- Magritte's work explores the relationship between reality and representation, asking viewers to consider how we perceive and understand the world around us.
- Magritte's paintings often feature a sense of humor and playfulness, inviting viewers to engage with the artwork on multiple levels.
- Magritte's artwork is known for its meticulous attention to detail and its use of precise, realistic rendering to create surreal and dreamlike images.
- Magritte's work challenges traditional ideas of perspective and composition, often presenting objects in unusual or unexpected ways.
- Magritte's paintings often feature a sense of ambiguity and contradiction, leaving viewers to question what is real and what is imagined.
- Magritte's use of repetition and variation in his artwork creates a sense of disorientation and uncertainty, challenging viewers to rethink their assumptions about the world.
- Magritte's work is known for its intellectual depth and philosophical complexity, exploring themes of perception, reality, and the nature of art itself.
- Magritte's paintings often feature visual puns and paradoxes, forcing viewers to question their assumptions and preconceptions about the world.
- Magritte's use of everyday objects in his artwork challenges viewers to reconsider the familiar and see the world in a new and unexpected way.
- Magritte's work has been exhibited in museums and galleries around the world, solidifying his reputation as one of the most important and influential artists of the 20th century.
- Magritte's paintings often feature elements of surprise and surrealism, creating a sense of wonder and mystery that captivates viewers.
- Magritte's work continues to inspire artists and thinkers today, challenging viewers to question their assumptions and explore the boundaries of perception and reality.
Analysis & Significance
Artistic Innovation
René Magritte’s surrealistic artworks challenged the traditional notions of reality and representation. His use of juxtaposition, unexpected combinations, and visual puns created a dreamlike world where familiar objects were transformed into mysterious, thought-provoking symbols. This innovative approach to art pushed boundaries and invited viewers to question their perceptions of the world around them.
Influence on Art History
Magritte’s work had a profound impact on later artists, particularly the Surrealist movement. His exploration of the subconscious mind, the power of imagination, and the relationship between words and images inspired a new generation of creators to delve into the realm of the irrational and the fantastical. Magritte’s legacy can be seen in the works of modern artists who continue to blur the lines between reality and illusion.
Cultural Significance Today
René Magritte’s art continues to captivate audiences around the world for its ability to challenge conventional thinking and spark imagination. His iconic paintings, such as “The Son of Man” and “The Treachery of Images,” have become symbols of philosophical inquiry and artistic exploration. Magritte’s unique vision, wit, and creativity have solidified his status as a master of surrealism and a timeless figure in the history of art.
René Magritte: An Analysis Games
Take Your Learning Offline
Want a convenient, print-ready study guide for this lesson? Become a Memory Wizards Pro member to unlock the downloadable " Memory Scrolls" for this topic and our entire library!
- ✓ Complete Vocabulary Lists
- ✓ Key Facts & Timelines
- ✓ Beautifully Formatted for Print & Mobile
Dive Deeper

Magritte: The Mystery of the Ordinary, 1926-1938
Written by renowned curator Anne Umland, this book provides a comprehensive exploration of René Magritte's work during the crucial years of 1926-1938, making it an essential read for anyone interested in delving into the enigmatic world of the surrealist artist.
View on Amazon
The Son of Man Poster
Rene Magritte's iconic painting 'The Son of Man Poster', offering valuable insights into the artist's unique style and symbolism.
View on AmazonTo help us keep Memory Wizards running and create more magical learning content, we are a participant in the Amazon Associates Program. If you make a purchase through the links on this page, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you. We only recommend resources we believe in.




